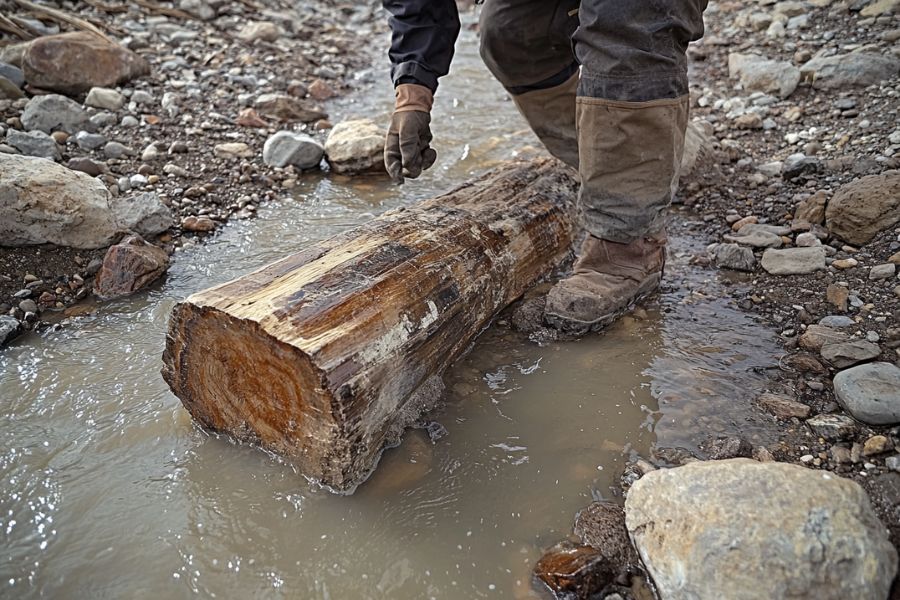
From the Missouri River in the east to the High Plains in the west, and from South Dakota’s border in the north to Kansas in the south, Nebraska offers hidden treasures for rock enthusiasts.
With over 77,000 square miles across vastly rural landscapes, the task of locating the top sites can be daunting. But fear not! We’ve done the hard work for you.
This guide reveals the 70 best locations to discover petrified wood across the Cornhusker State. We’ve meticulously researched and compiled this list to save you time and energy.
Get ready to explore Nebraska’s geological wonders and uncover ancient fossilized trees with confidence.
Petrified wood you can find in the US
In the United States, several types of petrified wood can be found, each with unique characteristics based on the original tree species and the minerals involved in the fossilization process. Here are some of the types you’ll be able to find.
Araucarioxylon
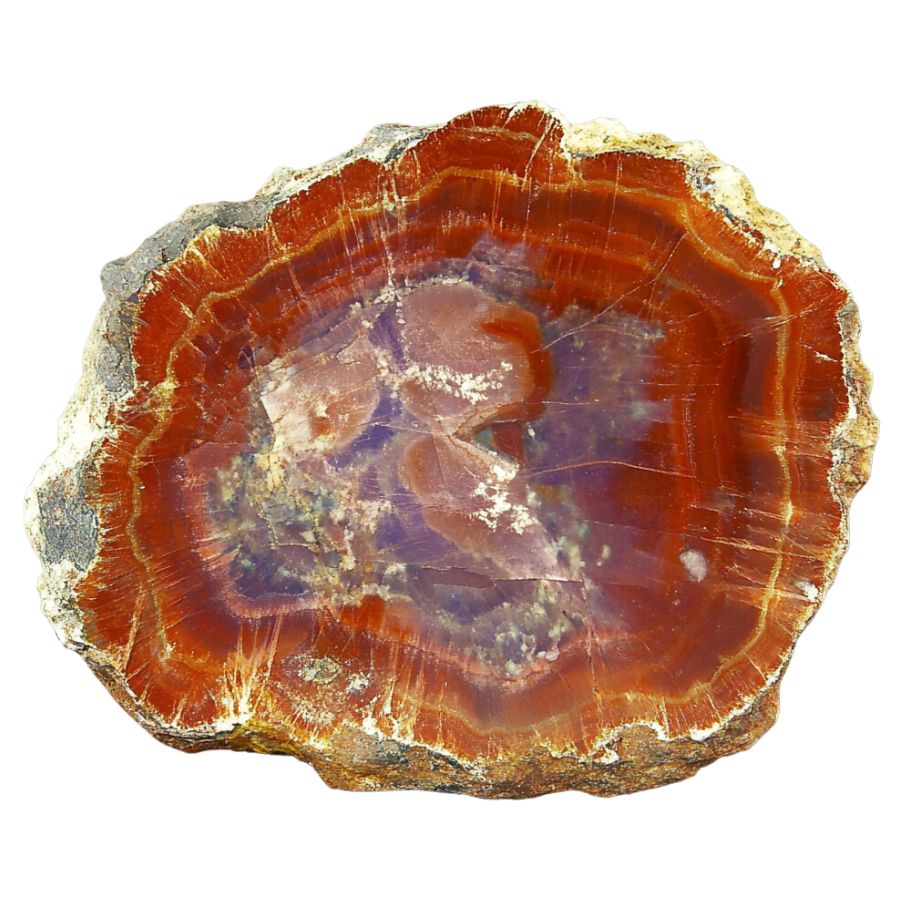

Found in the Petrified Forest National Park in Arizona, this is one of the most famous types of petrified wood. It comes from an extinct species of conifer. As Arizona’s state fossil, Araucarioxylon holds a special place in the state’s natural history.
These trees once formed vast forests during the Late Triassic period, about 225 million years ago. The vibrant colors in this petrified wood come from minerals that replaced the original tree material over time.
Metasequoia
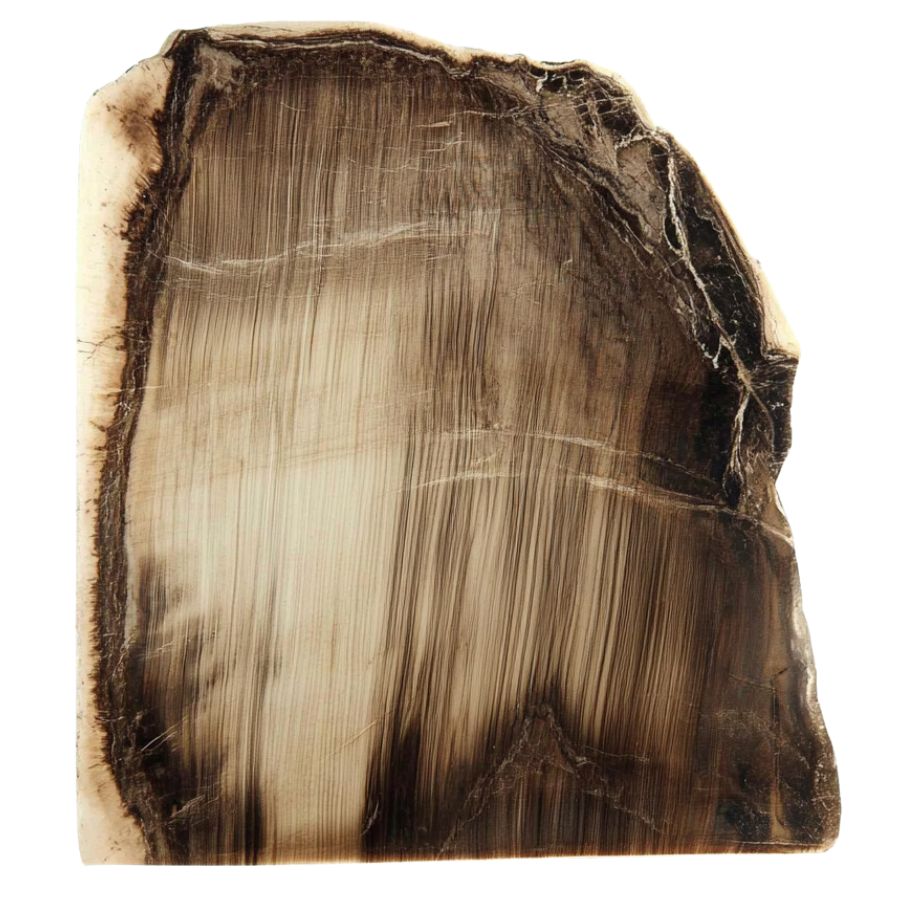

Often referred to as dawn redwood, this type of petrified wood can be found in various parts of the U.S., including the Pacific Northwest. Metasequoia was once thought to be extinct until living trees were later discovered in China.
Furthermore, its fine grain and reddish-brown color are characteristic features.
Palmoxylon
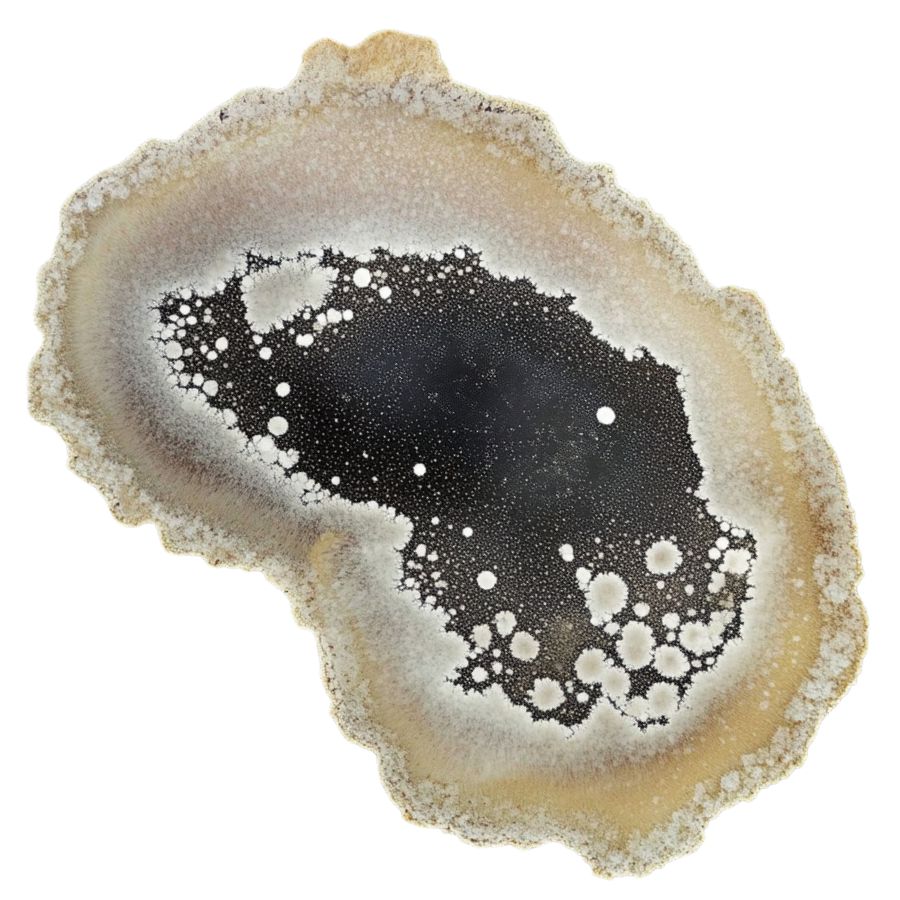
This petrified wood originates from palm trees and is often found in the Gulf Coast states like Texas and Louisiana. Recognized as the state stone of Texas, Palmoxylon is abundant and holds cultural significance.
The wood’s unique speckled or dotted pattern comes from the vascular bundles of the original palm tree. These fossils date back to the Cretaceous period, when the area was tropical and teeming with life.
Taxodium
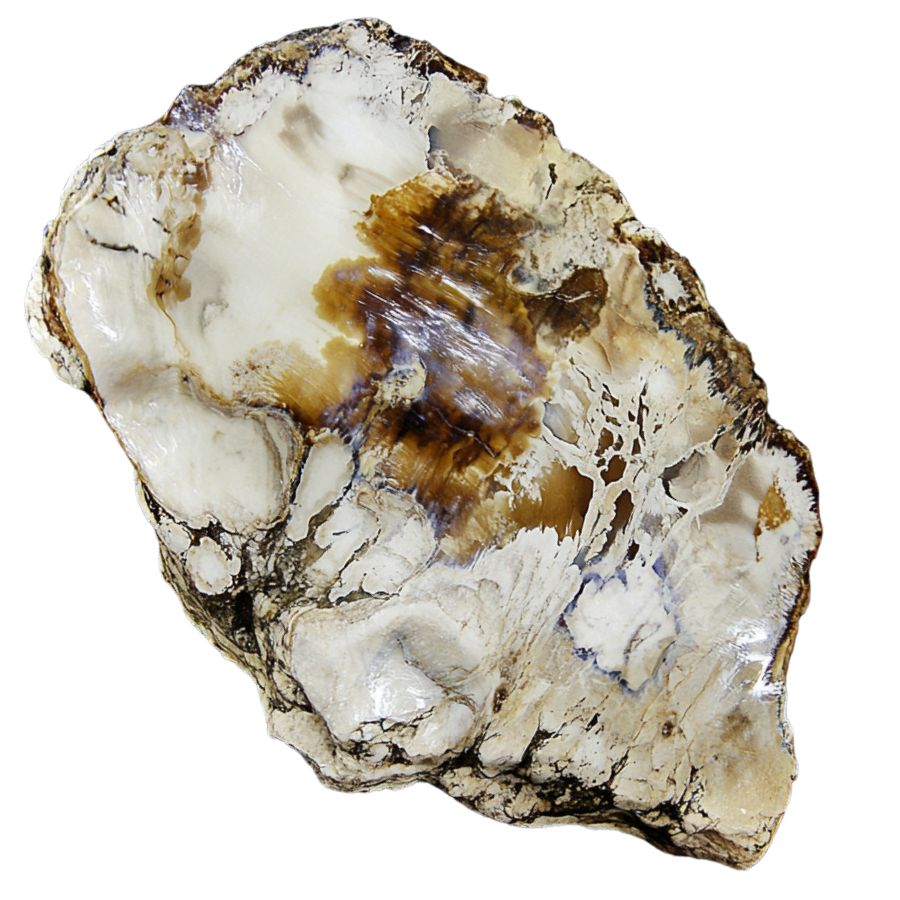

Also known as bald cypress, this petrified wood can be found in the southeastern U.S., particularly in areas that were once swampy. Taxodium wood is often found in places that were ancient swamps, where these trees thrived millions of years ago.
The wood is durable and shows intricate grain patterns, with growth rings and knotholes that tell the story of its long history. It’s a fascinating glimpse into the wet environments that once dominated the Southeast.
Sequoioxylon
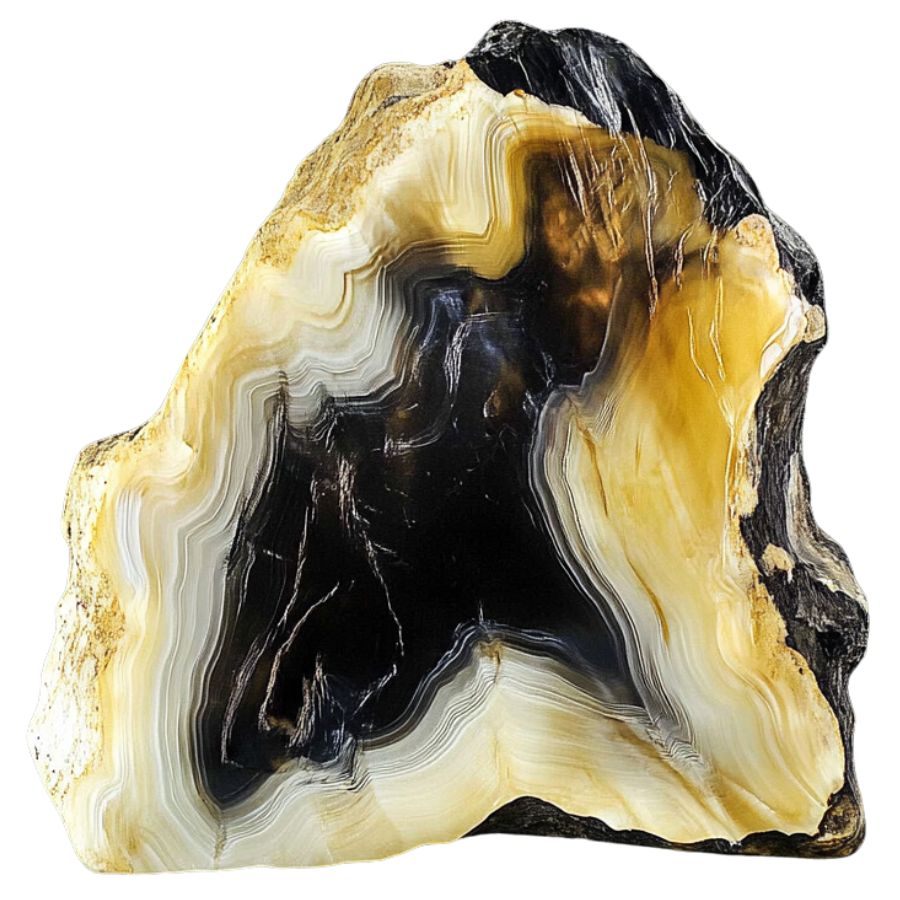

Petrified wood from ancient sequoia trees, found in places like California, where sequoia forests once thrived. These trees are the ancestors of the giant sequoias that still stand in California today.
The petrified wood is notable for its large, straight grain and reddish color, reflecting the immense size and age of the original trees.
Ginkgoxylon
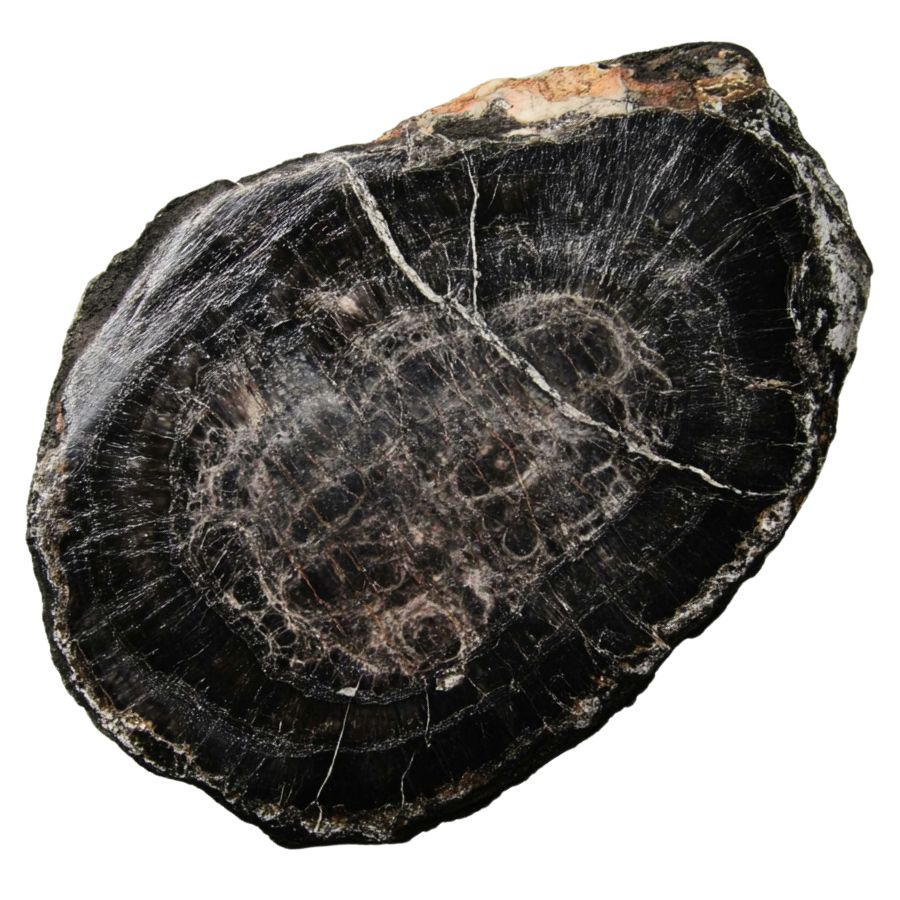

Petrified wood from ancient ginkgo trees, which can sometimes be found in states like Oregon and Washington. Ginkgo is one of the oldest tree species on Earth, with fossils dating back over 200 million years.
Ginkgo petrified wood often has a light color and may show patterns similar to the fan-shaped leaves of the living ginkgo.
Dicotyledonous Wood
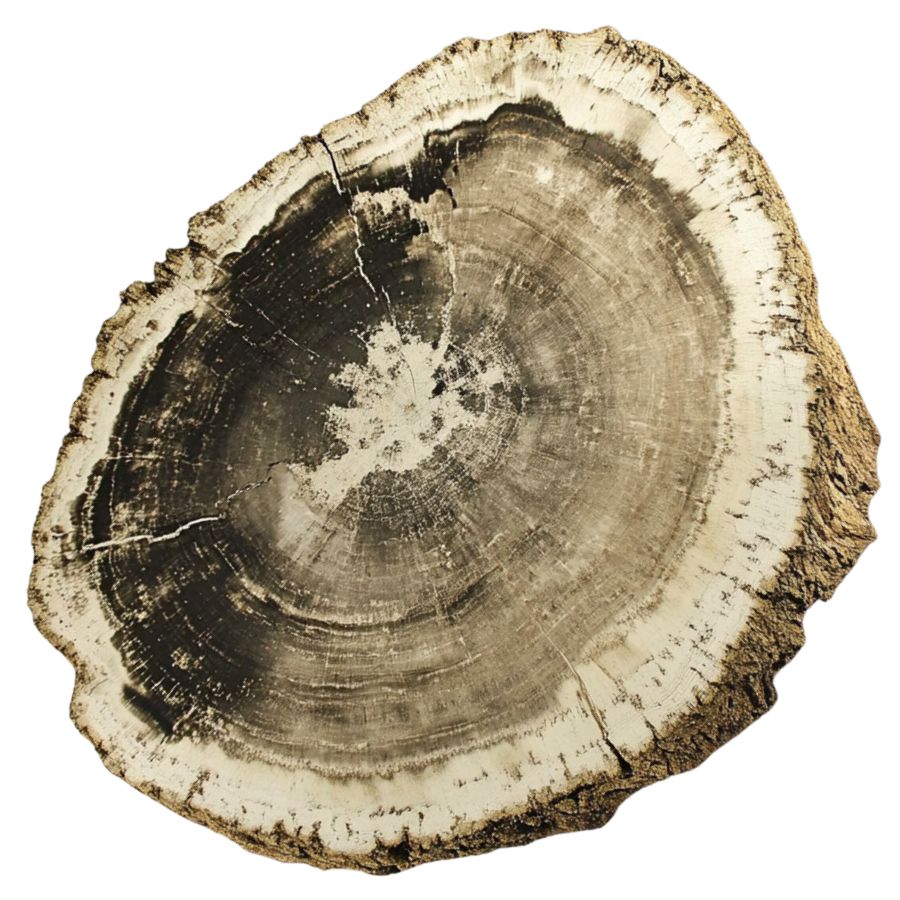

Found across various states, this type of petrified wood comes from broadleaf trees, making it more common and varied in appearance. You can spot dicotyledonous wood by the distinct vessels and growth rings that indicate seasonal changes.
This type of petrified wood is often found in regions that were once temperate forests, offering clues about the diverse plant life that existed millions of years ago.
Piceoxylon
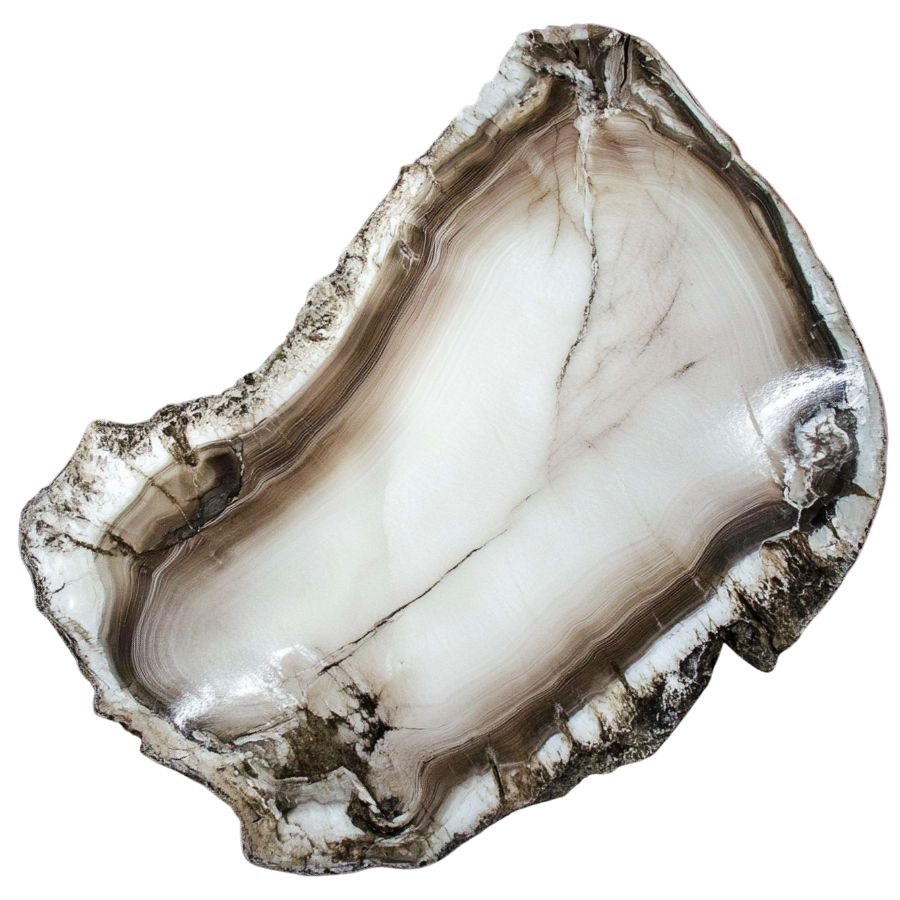
Petrified wood from ancient spruce trees, commonly found in areas like Wyoming and Montana, where coniferous forests once thrived. Piceoxylon is known for its straight grain and pale color, often showing growth rings that tell the tree’s life story.
These trees were part of the ancient boreal forests that covered large parts of North America during cooler periods.
A Quick Request About Collecting
Always Confirm Access and Collection Rules!
Before heading out to any of the locations on our list you need to confirm access requirements and collection rules for both public and private locations directly with the location. We haven’t personally verified every location and the access requirements and collection rules often change without notice.
Many of the locations we mention will not allow collecting but are still great places for those who love to find beautiful rocks and minerals in the wild without keeping them. We also can’t guarantee you will find anything in these locations since they are constantly changing.
Always get updated information directly from the source ahead of time to ensure responsible rockhounding. If you want even more current options it’s always a good idea to contact local rock and mineral clubs and groups
What Rough Petrified Wood Looks Like
Most of the photos you find of petrified wood are pieces that have been cut and polished. That is certainly useful but isn’t super helpful once you are out in the field. This is what you should look out for once you start hunting:
Exteriors like this
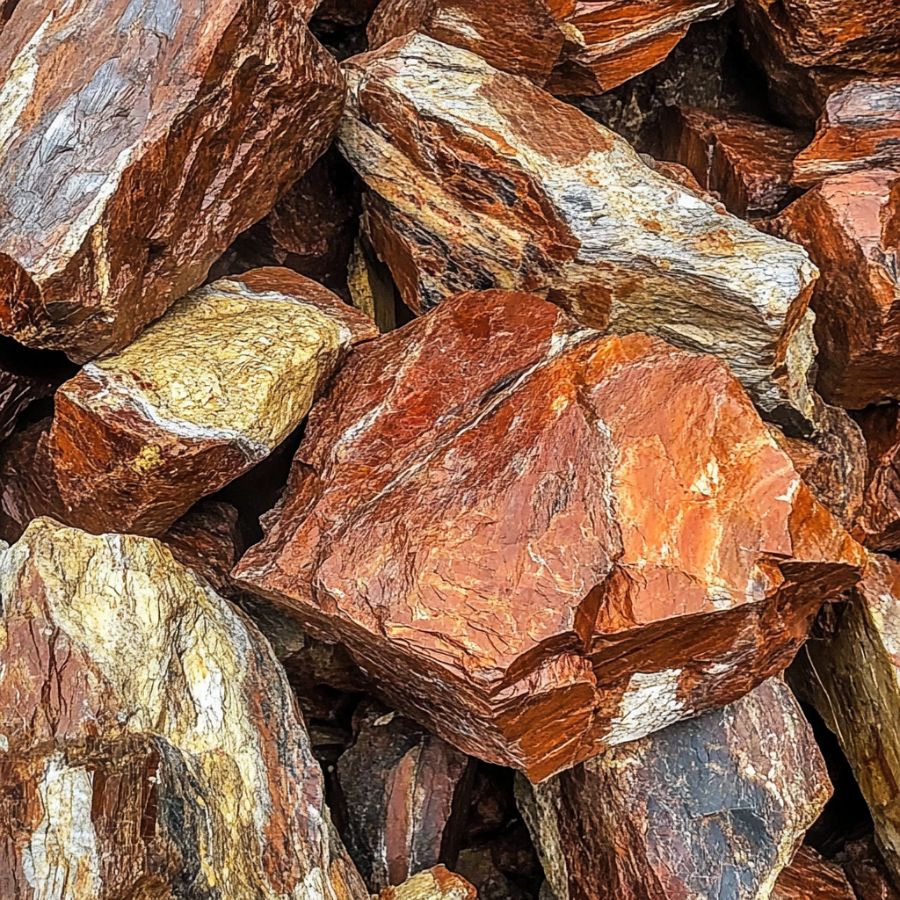

Every type of petrified wood has a different exterior and pattern but this is a good starting point on what to look for.
Texture and grain patterns
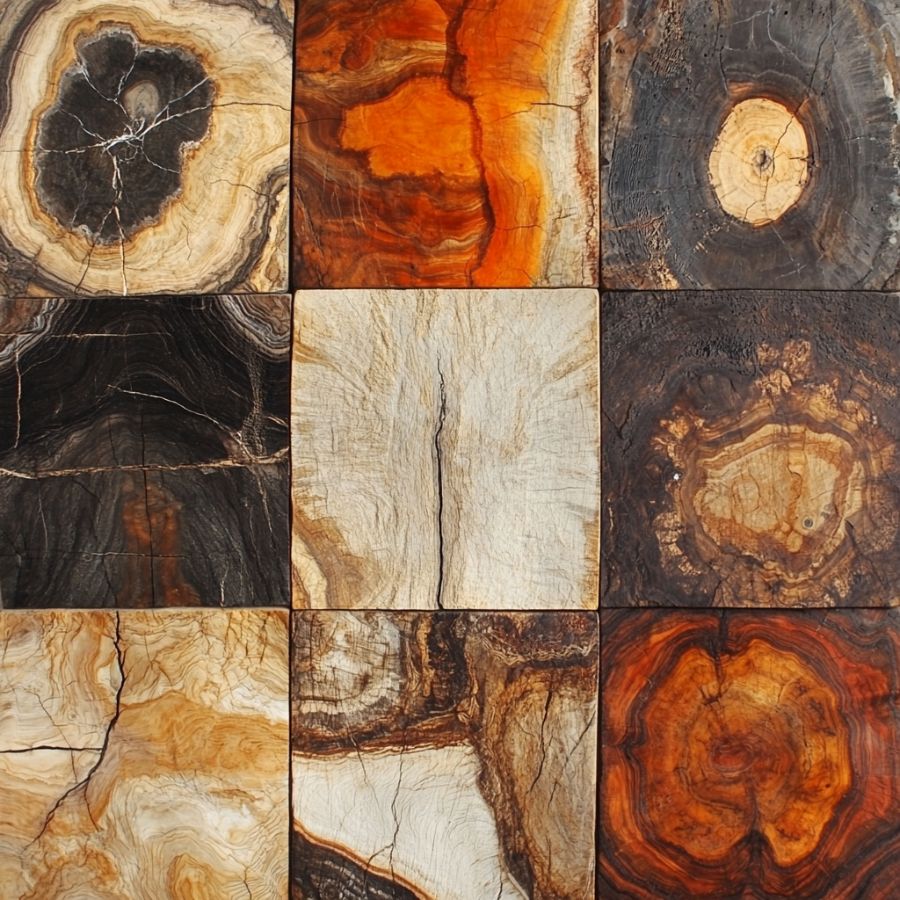

One of the most distinctive features to look for is the texture and grain patterns. Petrified wood often retains the original structure of the tree, including the grain, knots, and even growth rings. These patterns can appear similar to modern wood but are typically more rigid and fossilized.
Examine the surface for any linear patterns or striations that indicate the original wood grain. The texture may feel smoother or more polished in certain areas where mineralization has created a glassy effect.
Coloration and mineralization
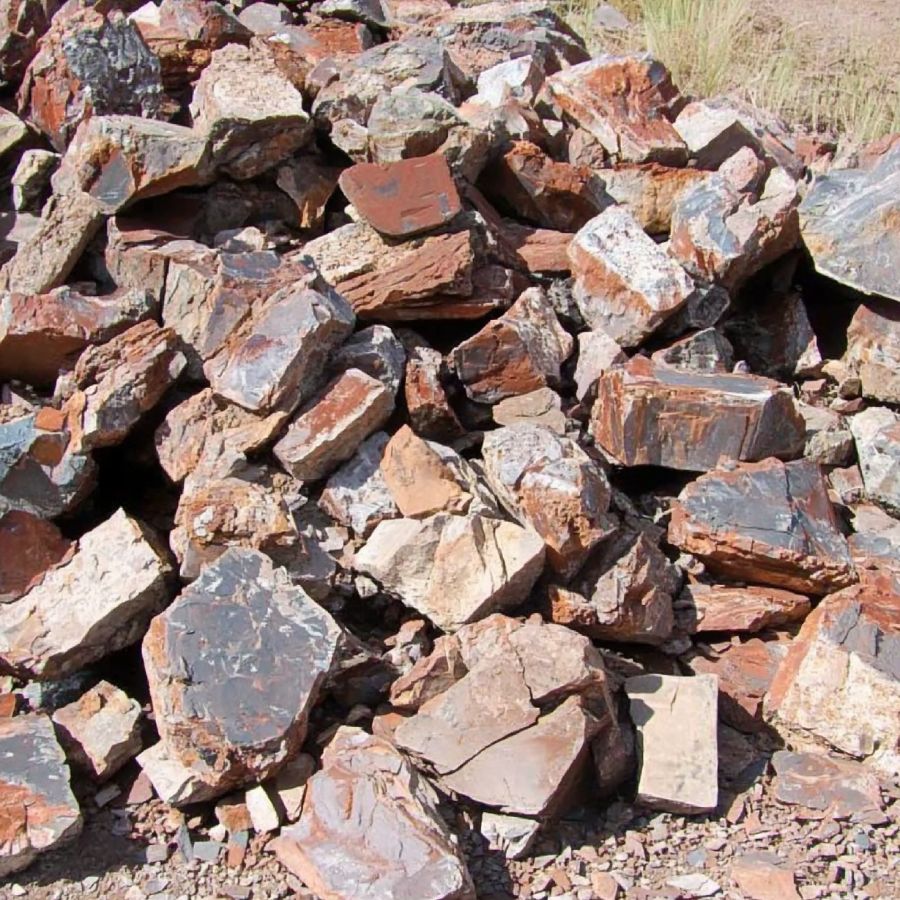

The color of petrified wood can vary significantly due to the minerals that replaced the organic material during the fossilization process. Common colors include shades of brown, red, yellow, orange, and black.
Some pieces might even exhibit multiple colors in intricate patterns. These colors are often more vivid and diverse than those found in regular rocks. When inspecting potential petrified wood, look for these distinct and varied hues, which can indicate the presence of different minerals such as silica, iron, manganese, and others that contributed to the petrification process.
Bark and exterior features
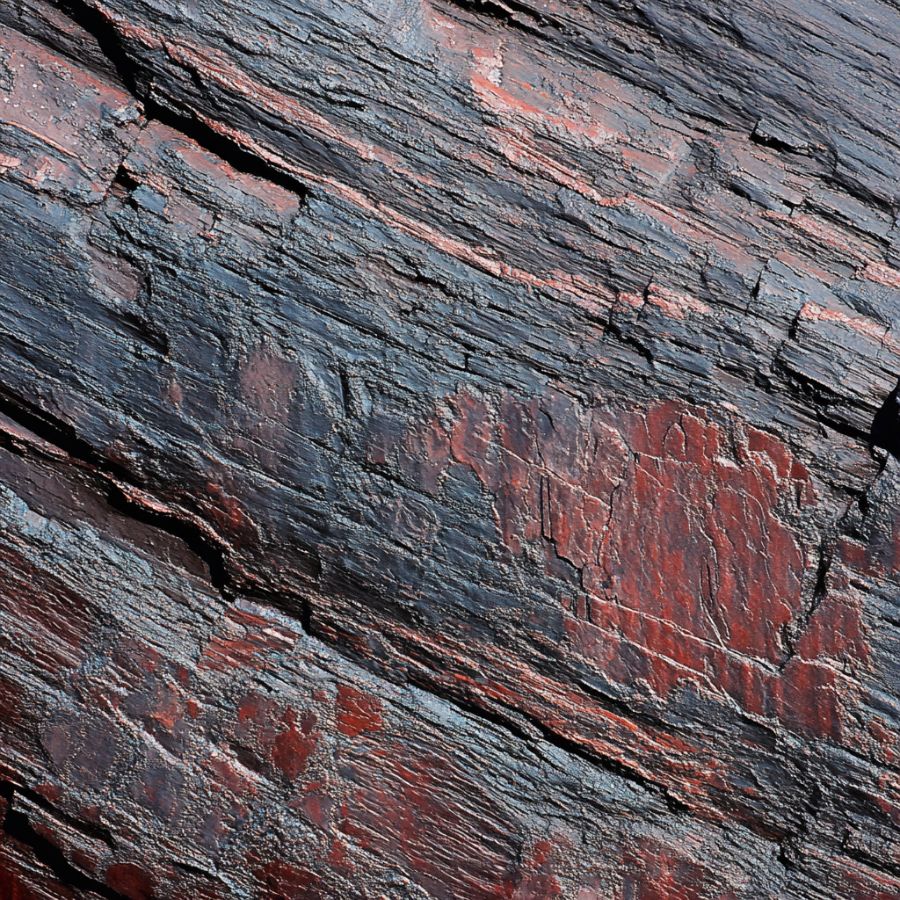

Another telltale sign of petrified wood is the presence of bark impressions or external textures that resemble tree bark. These features are often well-preserved and can include the rough, fibrous texture of bark, knots, or other surface irregularities typical of natural wood.
The exterior of rough petrified wood may also have a weathered appearance, with cracks and fractures that occurred as the wood fossilized over millions of years. Look closely for these natural wood features, as they can be a strong indicator that you have found a piece of petrified wood.
Weight and density
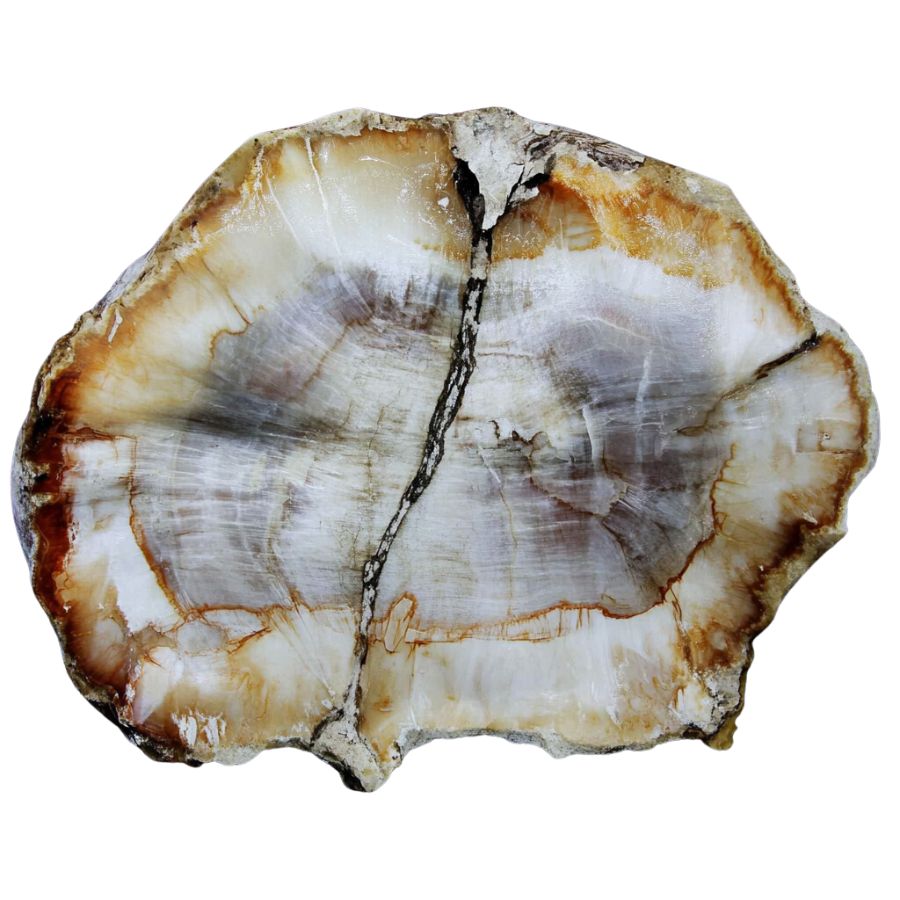

Petrified wood is typically much heavier and denser than regular wood due to the mineralization process. When rockhounding, pick up the specimen to feel its weight. Even small pieces of petrified wood will feel significantly heavier than an equivalent-sized piece of non-fossilized wood.
This increased density is due to the replacement of organic material with minerals, making petrified wood feel more like a rock than wood. Comparing the weight and density of your find with known samples of petrified wood can help confirm its authenticity.
- The extensive local experience of our team
- Input from a variety of local rockhounds and rockhound groups
- The difficulty in accessing a location
- Safety and potential hazards when collecting
- Private and public locations
- A desire to include locations for both the experienced and newbie hunters who are just starting out
Using these inputs we think we’ve put together the best list out there for those who love finding petrified wood for our collections!
General Areas To Try First

Before we get into the specific places you should be looking we wanted to give you some more general advice. Once you get to your hunting area you should head straight for these areas if you want to have the best results:
Lakeshores
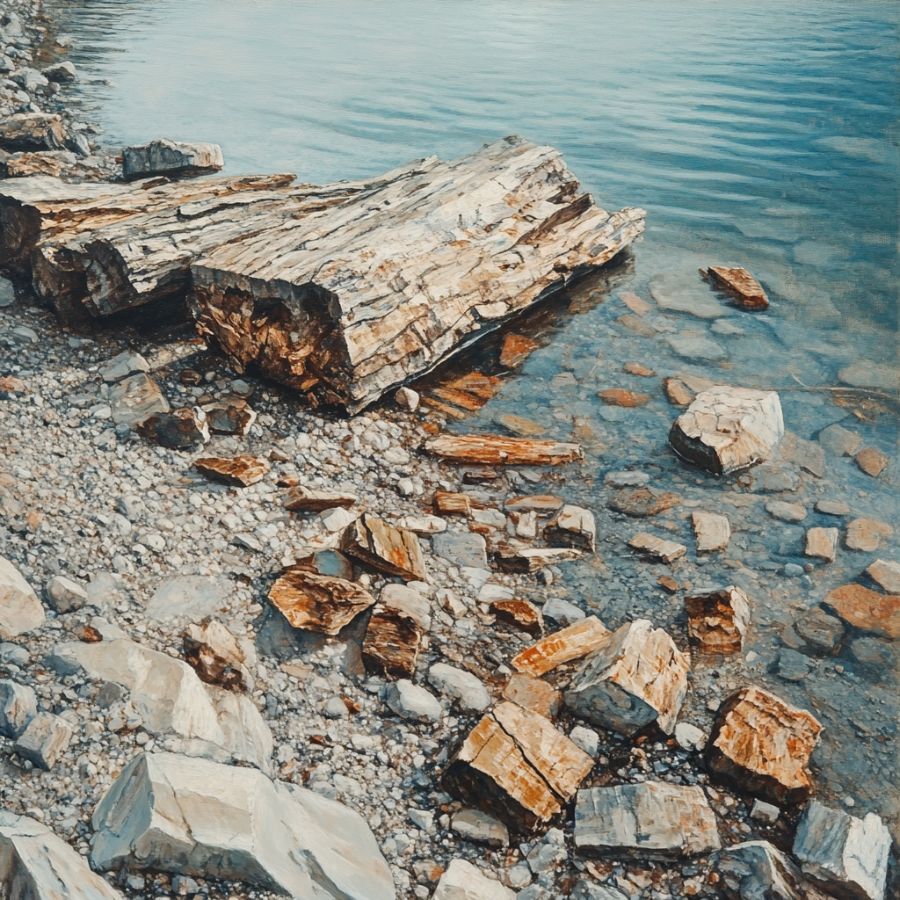

Lakeshores are like natural garbage cans because all things wash up and get left there over time. That includes wood that has turned to stone. As the water rises and falls, it carries sediment and rocks. It also takes the fossilized remains of trees from long ago.
Most lakeshores have a variety of rocks and minerals, which makes them an excellent place for petrified wood to grow and thrive. You’ll find a nice mix of sedimentary and volcanic rocks, the best sites for preserving wood fossils.
Roadcuts
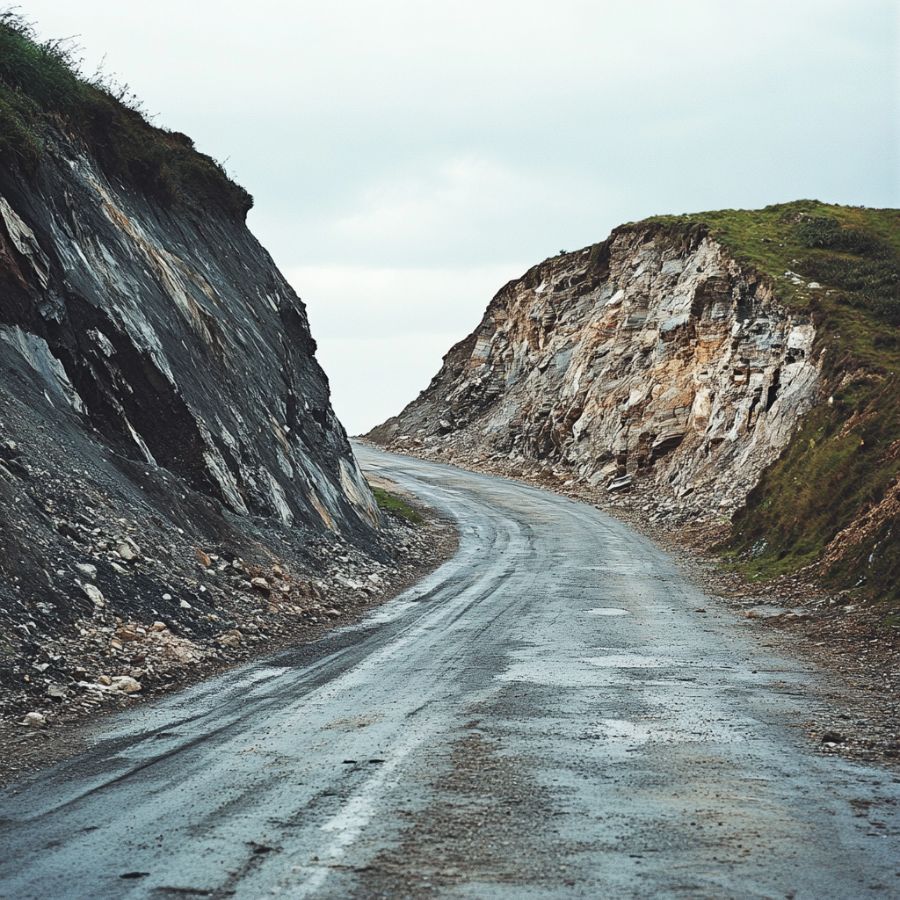

When building roads, parts of the ground are often cut away to make a smooth path. The magic happens when the road cuts through layers of rock and soil. Petrified wood is often buried deep underground, and roadcuts let us see these underground wonders.
As workers blast through the rock layers, they accidentally find petrified wood that has been there for hundreds of years. Petrified wood is easy for collectors to spot because the exposed rock layers of roadcuts make it easy to see its unique patterns and colors.
Streams and creeks
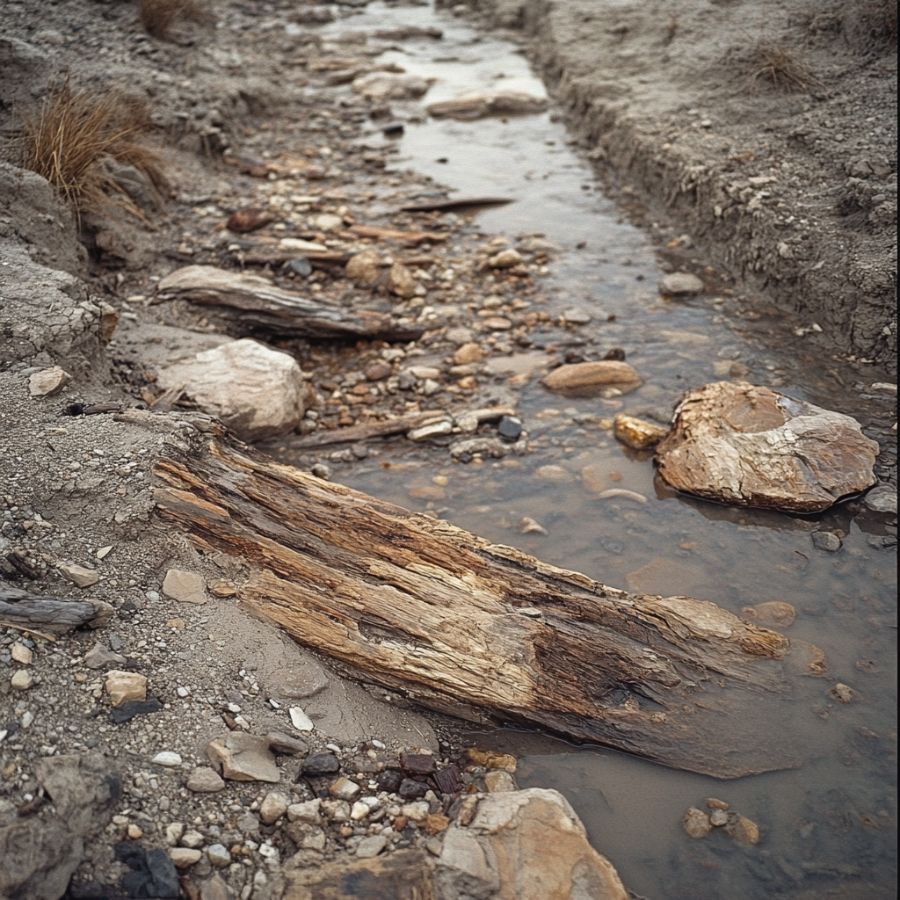

Streams and creeks can move loose sediment away, which can reveal old wood that has turned to stone. As the water moves around, it exposes small pieces or even more significant amounts of petrified wood that have settled on the streambed.
Streams and creeks are more accessible for collectors because they are not as big. You can easily walk along their banks, jump from rock to rock, and look for petrified wood at the water’s edge.
River beds
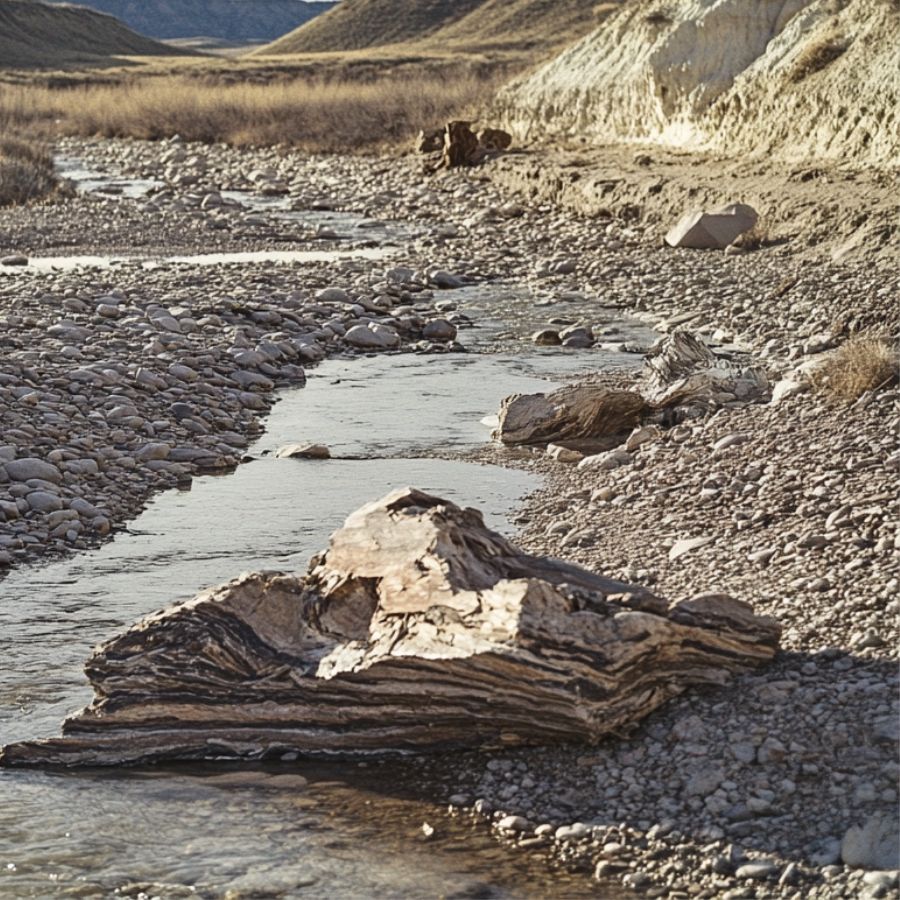

Riverbeds are excellent for finding petrified wood due to their unique geological and environmental conditions. Rapid burial by sediments like sand, silt, and mud protects fallen trees from decay, initiating the fossilization process.
Mineral-rich waters flowing through rivers facilitate the replacement of organic material with minerals such as silica, turning wood into stone. Over time, erosion exposes these buried treasures, making them accessible for discovery.
This dynamic environment, with constant sediment deposition and mineral infiltration, creates ideal conditions for the formation and eventual exposure of petrified wood.
Types of Petrified Wood Found in Nebraska
In Nebraska, several types of petrified wood can be found. The most common types discovered in Nebraska are opalized wood, agatized wood, palm wood, and cottonwood.
Opalized wood is formed when silica-rich water replaces the original wood structure, resulting in a colorful, opal-like appearance. Agatized wood is similar but has a more banded or striped pattern.
Palm wood and cottonwood are specific tree species that have undergone the petrification process.
Palm wood is rare in Nebraska and indicates a warmer climate in the past. Cottonwood is more common and reflects the region’s more recent natural history.
The Best Locations For Finding Petrified Wood in Nebraska
Exploring the top places in the state can significantly boost your chances of finding crystals. By focusing your search on these well-regarded locations, you’ll be well on your way to uncovering some of the state’s hidden gems.
DON'T MISS OUT ON ANY GREAT FINDS!
While you're out searching for Petrified Wood you're going to find A LOT of other interesting rocks and minerals along the way. The last thing you want to do is toss out something really interesting or valuable. It can be easy to misidentify things without a little guidance.
We've put together a fantastic field guide that makes identifying 140 of the most interesting and valuable rocks and minerals you will find REALLY EASY. It's simple to use, really durable, and will allow you to identify just about any rock and mineral you come across. Make sure you bring it along on your hunt!
Stinking Water Creek

Stinking Water Creek is located in the southwestern part of Nebraska, specifically in Chase County. This picturesque stream, nestled in the Great Plains, is renowned for its rich geological history and unique formations.
Petrified wood has been found in this area, making it a popular spot for rockhounds. The creek’s banks are lined with sedimentary rocks, which help preserve these fossilized treasures.
Visitors can find petrified wood scattered in the gravels and along the creek bed. The constant flow of water reveals and transports these ancient pieces, making them more accessible for collectors.
Keya Paha River

The Keya Paha River, located in the north-central part of Nebraska, flows southeast through Cherry County, showcasing a stunning landscape of rolling hills and agricultural fields.
The river’s name, derived from the Dakota word for “turtle hill,” reflects the region’s natural beauty and significance.
This area is rich in geological history, with sedimentary rock formations that reveal a variety of minerals. Petrified wood can be found here, often discovered in the gravel beds and along the creek banks.
The river’s continuous flow exposes these ancient treasures, making it a prime spot for rockhounds. Unique geological features, such as the draws and washes, enhance the hunting experience, as they often reveal hidden specimens.
Collectors can explore the gravels and creek beds to uncover pieces of petrified wood, which are prized for their beauty and historical value, making the Keya Paha River a must-visit for gemstone enthusiasts.
Grand Island

Grand Island, located in the heart of Nebraska, is a prime destination for petrified wood enthusiasts. This city, situated in Hall County, boasts a rich geological history that includes ancient river systems and glacial movements.
The alluvial plains surrounding Grand Island provide an ideal setting for finding various types of rocks and minerals, including petrified wood.
One of the most fascinating aspects of Grand Island is its exposure to gravel deposits, riverbanks, and creek beds.
These locations are particularly promising for rockhounding, as natural processes have exposed and transported petrified wood over time.
Elm Creek Area
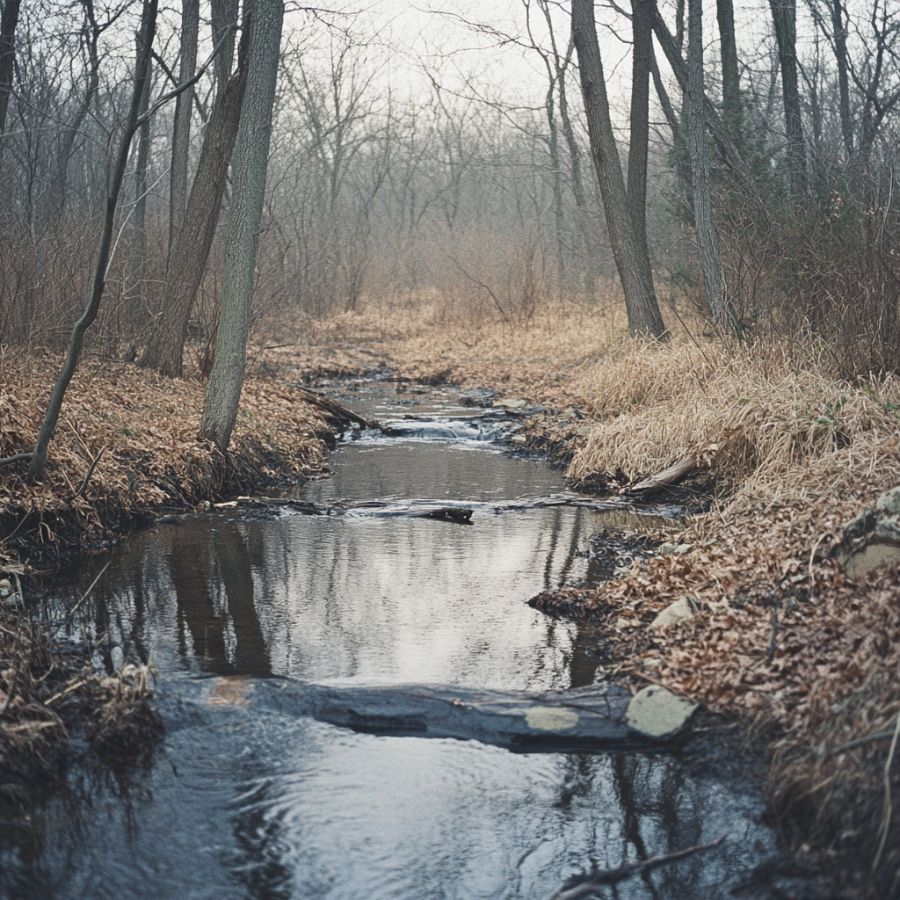

Elm Creek is a charming village in Buffalo County, nestled near the Platte River. This area is renowned for its rich geological history, making it a prime spot for finding petrified wood.
The ancient riverbeds and sediment deposits here have preserved these fossilized remnants of trees, which can often be discovered in the gravel beds along the creek banks.
Rockhounding enthusiasts flock to Elm Creek for its diverse mineral deposits, including agates and jasper. The proximity to the Platte River enhances the area’s potential for uncovering petrified wood, especially after heavy rains that wash away surface materials.
Whether you’re searching the banks or sifting through gravel, Elm Creek offers a unique opportunity to connect with Nebraska’s prehistoric past while enjoying the beauty of the landscape.
Pine Ridge

Nestled in the rugged northwest corner of Nebraska, the Pine Ridge area in Dawes County is a prime destination for petrified wood enthusiasts.
This unique escarpment, characterized by its Ponderosa Pine-covered hills and rocky outcrops, is a testament to the region’s fascinating geological history.
Ancient sedimentary deposits and volcanic ash layers have created an environment rich in various minerals and fossils, making Pine Ridge a true rockhounding paradise.
Petrified wood can be found in abundance throughout the area’s gravel beds, washes, and draws. Exploring the banks of creeks and rivers, as well as the exposed sediment layers, can yield stunning specimens of this fossilized treasure.
The unique combination of sedimentary and volcanic activity has preserved these ancient plant remains, creating a window into the past that captivates both casual observers and avid collectors alike.
Our Other Favorite Places For Petrified Wood
After discussing our top picks, we wanted to discuss the other places on our list. Below is a list of the additional locations where we have succeeded, along with a breakdown of each place by county.
| County | Location |
| Adams | Ayr Area |
| Boyd | countywide in the gravels and roadcuts |
| Brown | Ainsworth Area |
| Cherry | Crookston Area |
| Cherry | Valentine |
| Cherry | Spring Creek |
| Cheyenne | Sidney Area |
| Cheyenne | Gurley Area |
| Clay | Deweese Area |
| Cuming | gravels in the West point |
| Dawes | Whitney Area |
| Dawes | Crawford Area |
| Dawes | Chadron Area |
| Dawson | Cozard Area |
| Dawson | Gothenburg |
| Dawson | Lexington |
| Deuel | Big Springs Area>/td> |
| Dodge | Fremont Area |
| Dundy | Benkelman |
| Franklin | Bloomington |
| Furnas | Arapahoe Area |
| Furnas | Beaver City |
| Furnas | Oxford |
| Gage | Holmesville |
| Gage | Wymore |
| Garden | Lewellen |
| Garden | Lisco Area |
| Garfield | Burwell Area |
| Hall | Wood River |
| Buffalo | Kearney |
| Douglas | Omaha |
| Jefferson | Powell Area |
| Jefferson | Steele City |
| Jefferson | Fairbury Area |
| Morril | gravels in the Bayard Area |
| Nance | Fullerton Area |
| Nance | Genoa Area |
| Nemaha | gravel beds of the Little Nemaha River |
| Nemaha | Johnson Area |
| Nuckolls | Oak Area |
| Scotts Bluff | Layman Area |
| Scotts Bluff | Mitchell Area>/td> |
| Scotts Bluff | in rd. cut on Hwy. 87 |
| Sheridan | Whiteclay Area |
| Sheridan | Kay Springs Area |
| Sheridan | Hat Springs |
| Saunders | Ashland Area |
| Sioux | Orella Station Area |
| Cheyenne | Lodgepole Creek |
| Brown | Niobrara River Valley |
| Dawes | White River |
| Butler | Bellwood Area |
| Cass | South Bend Area |
| Furnas | Oxford |
| Keith | Ogallala Area |
| Keith | Sarben Area |
| Lincoln | Hershey Area |
| Lincoln | North Platte Area |
| Lincoln | Maxwell Area |
| Thayer | Herbon Area |
| Phelps | Holdrege Area |
| Platte | Columbus Area gravel pits |
| Platte | Oconee Area |
| Polk | shorelines and adjacent sand pits of Osceola Area |
| Sarpy | La Platte Area |
Always Confirm Access and Collection Rules!
Before heading out to any of the locations on our list you need to confirm access requirements and collection rules for both public and private locations directly with the location. We haven’t personally verified every location and the access requirements and collection rules often change without notice.
Many of the locations we mention will not allow collecting but are still great places for those who love to find beautiful rocks and minerals in the wild without keeping them. We also can’t guarantee you will find anything in these locations since they are constantly changing.
Always get updated information directly from the source ahead of time to ensure responsible rockhounding. If you want even more current options it’s always a good idea to contact local rock and mineral clubs and groups


