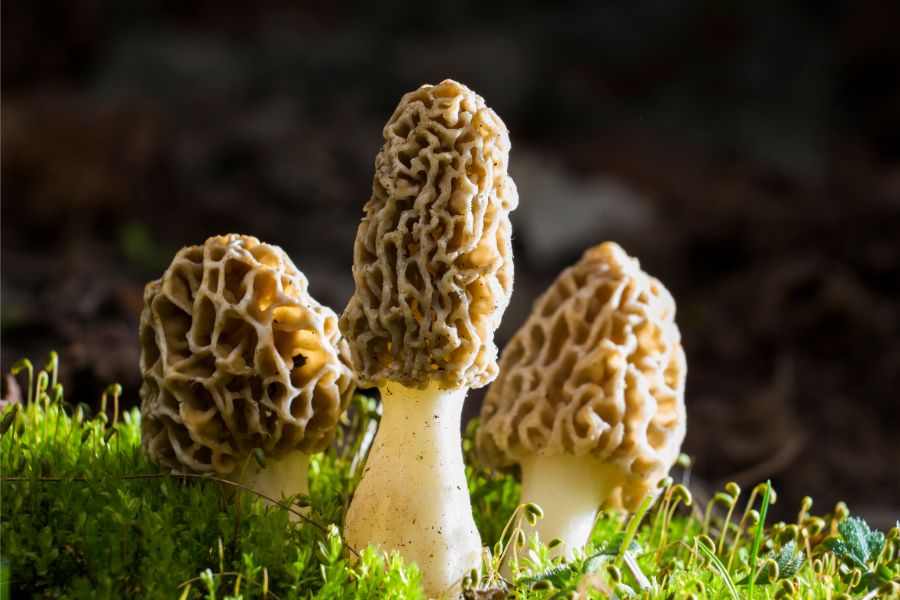
Morel season is one of my favorite times of year here in Mississippi. These tasty mushrooms pop up around our state, and finding them feels like striking gold. They’re worth their weight too, often selling for more than $50 a pound.
Our state has plenty of good spots where morels like to grow. You might find them in old apple orchards, near dead elm trees, or in forests after a good rain. Mississippi’s mix of woods and weather creates just the right conditions for these prized mushrooms.
Looking for morels connects us to an old Mississippi tradition of foraging. Our grandparents and great-grandparents knew the land well and what treasures it held. Many families still pass down special spots through generations like valuable family secrets.
The hunt itself brings so much joy. Walking through our beautiful forests in spring sunshine feels good for the soul. The excitement when you spot your first morel of the season is something all mushroom hunters understand.
Learning which trees morels like to grow near makes the search easier. The knowledge builds over time with each trip to the woods. Every year I get better at spotting the honeycomb pattern among fallen leaves.
What We Cover In This Article:
- What Morel Mushrooms Look Like
- Mushrooms That Look Like Morels But Aren’t
- How To Find Morels
- Where You Can Find Morels
- Additional locations to find Morels
- When You Can Find Morels
- The extensive local experience and understanding of our team
- Input from multiple local foragers and foraging groups
- The accessibility of the various locations
- Safety and potential hazards when collecting
- Private and public locations
- A desire to include locations for both experienced foragers and those who are just starting out
Using these weights we think we’ve put together the best list out there for just about any forager to be successful!
A Quick Reminder
Before we get into the specifics about where and how to find these plants and mushrooms, we want to be clear that before ingesting any wild plant or mushroom, it should be identified with 100% certainty as edible by someone qualified and experienced in mushroom and plant identification, such as a professional mycologist or an expert forager. Misidentification can lead to serious illness or death.
All plants and mushrooms have the potential to cause severe adverse reactions in certain individuals, even death. If you are consuming wild foragables, it is crucial to cook them thoroughly and properly and only eat a small portion to test for personal tolerance. Some people may have allergies or sensitivities to specific mushrooms and plants, even if they are considered safe for others.
The information provided in this article is for general informational and educational purposes only. Foraging involves inherent risks.
What Morel Mushrooms Look Like
The first thing you need to know if you want to be a successful morel hunter is what these mushrooms generally look like. There are several different types to look out for and they have certain differences that set them apart from each other:
Grey Morels
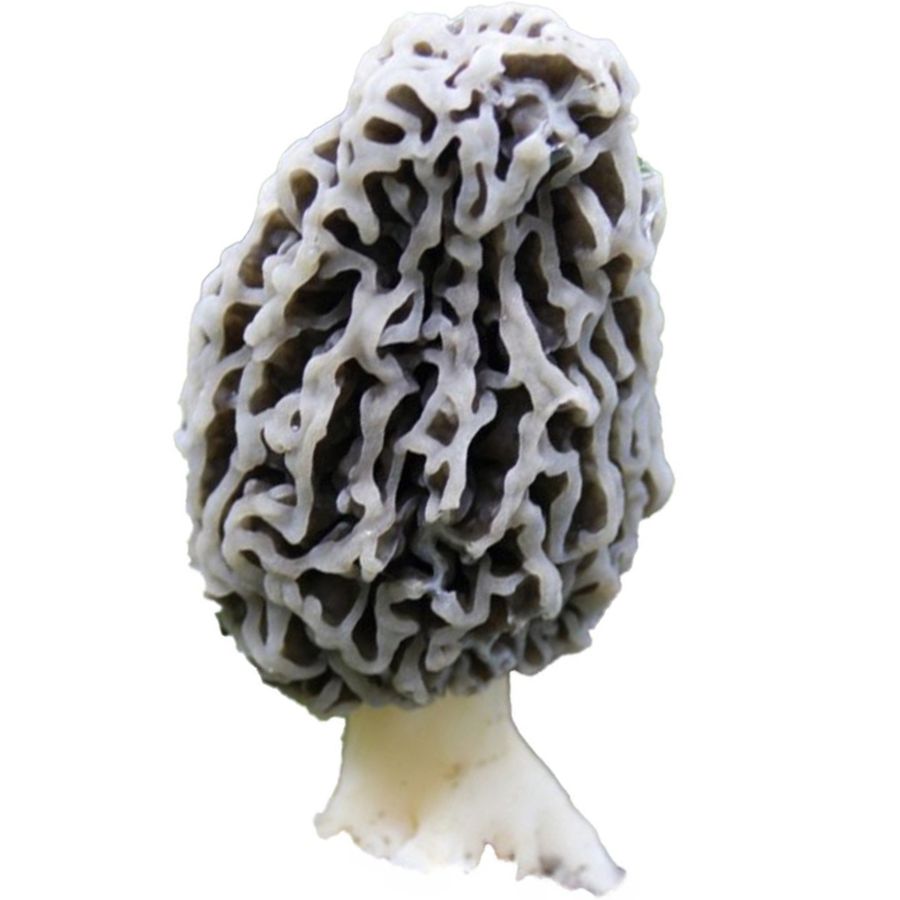

Grey morels (Morchella tomentosa) are also called fuzzy foot or fire morels. Their color can range from deep gray to blackish. They tend to grow in areas that have recently experienced wildfires, as they thrive in the nutrient-rich soil left behind by the fires.
Their caps have a ridged, honeycomb-like texture, similar to other morels. However, grey morels have caps that are covered in fine, fuzzy hairs, so they generally feel velvety to the touch. This is a key thing that sets them apart from other types of morels.
The stem of a gray morel also tends to be stouter and thicker, with an off-white color that can sometimes have a yellow-tinge. In addition, its flesh also tends to be denser compared to the more delicate flesh of yellow morels.
Cream or Yellow Morels
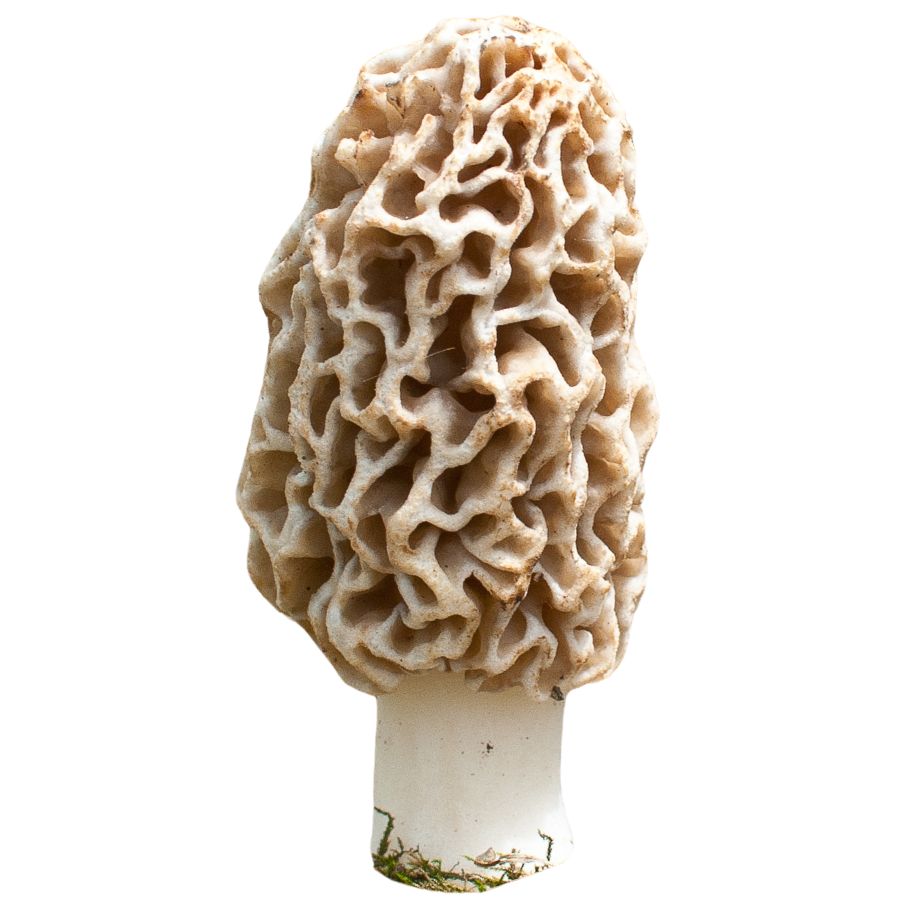

Yellow morels (Morchella esculenta), also known as common, cream, or sponge morels, are named for their yellowish or tan-colored caps. These morels have a honeycomb-like appearance, with deep ridges and pits. The ridges also tend to stay just a bit darker than the rest of the cap.
Pay close attention to the cap of the mushroom. The caps of yellow morels are characteristically fuller and rounder or oval-shaped. Also, their stems are hollow with a wide base and a pale creamy color.
This morel variety commonly grows in hardwood forests, especially near deciduous trees like ash, elm, and oak. They’re also one of the first morel varieties to appear in the spring.
Keep in mind that yellow morels start out with a more grayish appearance, gradually turning yellow as they grow older. This means that if you come across grayish morels in a hardwood forest, then they might be yellow morels that still need to mature.
Black Morels
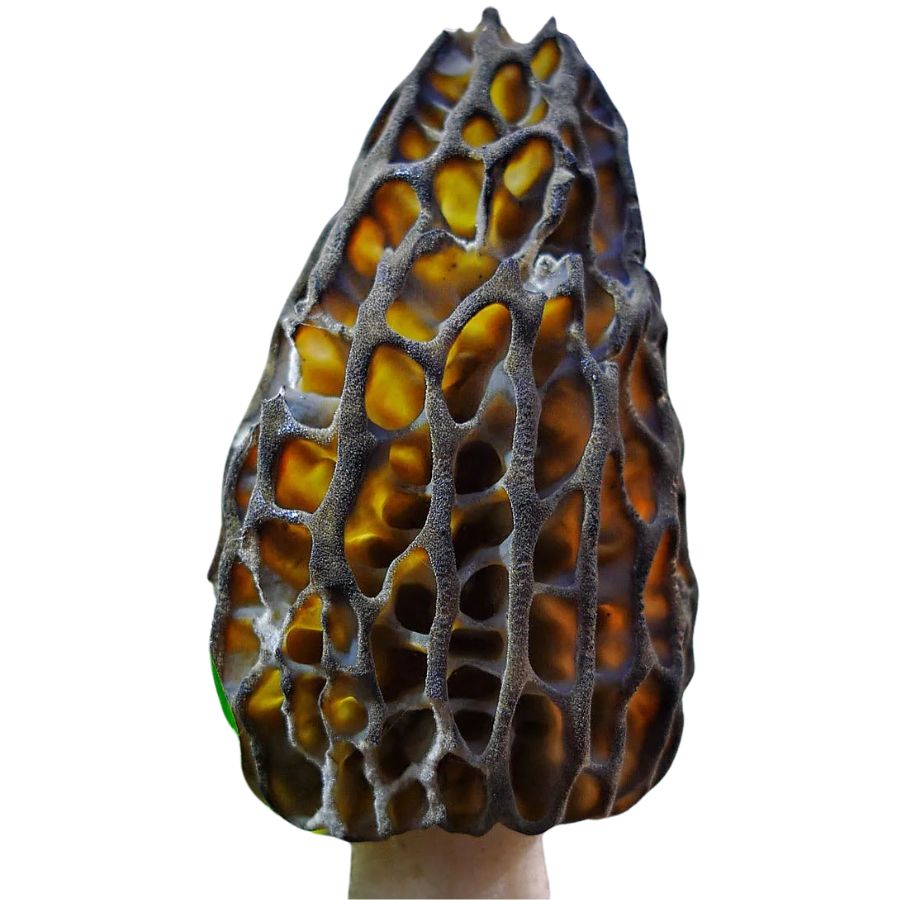

Black morels (Morchella angusticeps), sometimes called eastern black morels, are a distinctive variety of morel mushrooms known for their dark, almost black caps. Their caps have the same honeycomb-like surface seen in other morels, but they are often taller and more slender.
You can also expect the ridges of this morel type to be noticeably darker than the pits. The stem can be off-white to pale yellow, and is typically wrinkly with a wider base.
This morel variety is often found in hardwood forests and old orchards. They thrive in moist soil and areas around decaying trees and plants as well as areas near streams and creeks. While they grow in moist environments, they don’t like overly wet soil.
You can also expect to black morels in the early to mid-spring, and they emerge just a bit earlier than yellow morels.
For a full overview of what wild mushrooms are easy to recognize, check out this resource on easy-to-identify wild mushrooms.
Mushrooms That Look Like Morels But Aren’t
Now that you have a better idea of what to keep an eye out for when you’re hunting for morels, you’ll also need to know which mushroom species you have to avoid.
Consider exploring foraging for survival strategies that include avoiding toxic lookalikes.
These mushroom species may look a lot like morels, but they’re not morels. Here are the morel lookalikes that you need to be able to identify:
Early Morel – Verpa bohemica
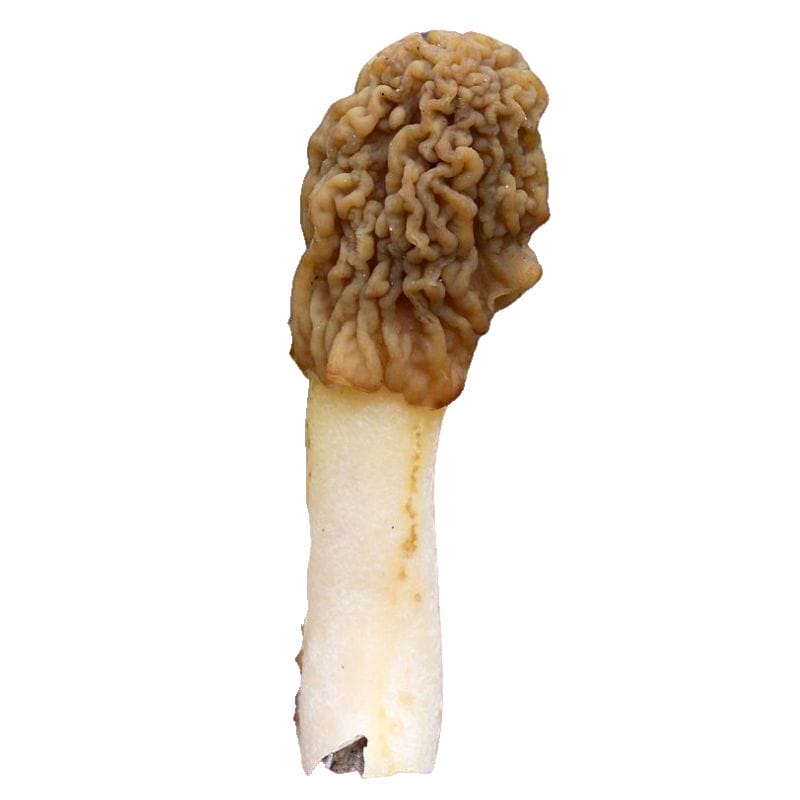

True to its name, the early morel (Verpa bohemica) is a morel lookalike that also emerges early in the spring. A lot of the time, it emerges even before true morels do! Add the fact that it looks like a morel to the unsuspecting eye, and it’s understandable that people often confuse it with the real thing.
The cap of the early morel is light brown or tan and looks kind of like a wrinkled thimble. It doesn’t have the distinctive ridges and deep pits that true morels have. The cap is also attached only to the top end of the stem, with the sides hanging over the stem, much like a bell.
Another difference between early morels and true morels is that early morels tend to have stems with fibers that look like cotton inside. The stems of true morels are generally hollow.
Can you eat the Verpa bohemica? The answer is…controversial, to say the least. Some say that these mushrooms are absolutely delicious and taste a lot like true morels. Others say that it’s fine and good enough to eat if you cook it for a long time. There also are those who only eat the stems and dispose of the caps.
In recent years, however, respected experts like Noah Siegel and Christian Schwarz, authors of Mushrooms of the Redwood Coast, have re-evaluated these fungi. They now list Verpa conica and Verpa bohemica as plain old “edible”—no scare quotes, no special warnings.
Globally, Verpa mushrooms are commonly eaten and even sold commercially without issue. Much of the lingering stigma seems to stem from U.S.-based caution, often due to a lack of deeper knowledge. For a thorough look at this debate, check out the detailed coverage by Fungi Magazine.
Bell Morel – Verpa Conica
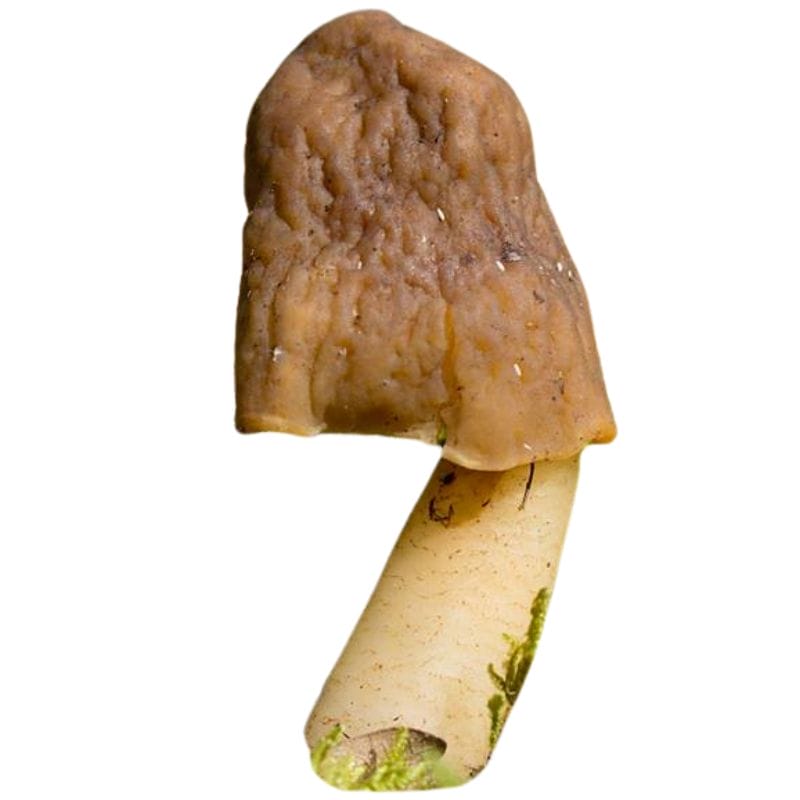

Like early morels, the bell morel (Verpa conica) is also easy to confuse as a true morel. However, it does have a few distinguishing characteristics.
Notably, the cap of bell morels is more similar to the cap of early morels. The cap is attached only to the top end of the stem, with the sides hanging down. It looks a lot like a bell — hence the name!
However, unlike the cap of early morels, the cap of bell morels doesn’t have a wrinkled appearance.
The stem of the bell morel is white to pale yellow, and also longer and narrower compared to the stems of true morels and early morels. It also has a smoother and more fibrous texture, though it has a similar cottony interior as early morel stems.
As a general rule, bell morels should be cooked thoroughly before consumption. If you’re eating it for the first time, it’s best to only eat small portions at first to test your tolerance and avoid gastrointestinal issues.
False Morel – Gyromitra esculenta
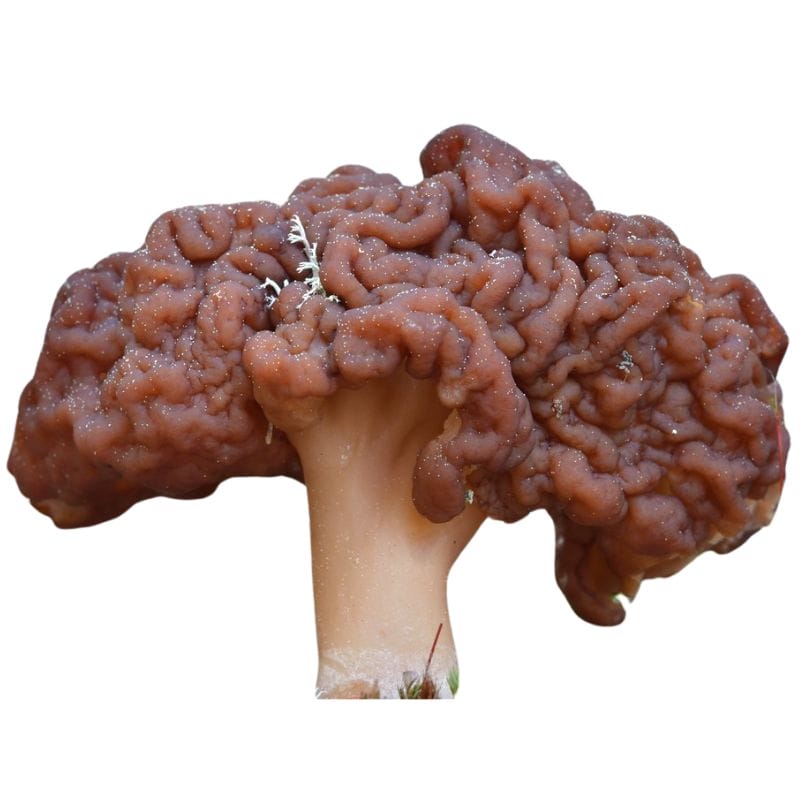
False morels (Gyromitra esculenta) are a type of mushroom that you definitely need to watch out for. It’s a toxic mushroom that unfortunately looked quite similar to true morels. Luckily, there are key differences between true and false morels that can help you set the two apart.
One thing that you might be able to notice right away is the appearance of the cap. The cap of a false morel is wrinkled, not sharply ridged and pitted like the cap of a true morel. You’ll also notice that false morel caps are wider where true morel caps are narrower.
Overall, false morels look a lot like brains.
In addition, false morels have a reddish brown to dark brown color, sometimes tinged with yellow or tan. The stem also tends to be short and thick, with an off-white to yellow color and a cottony, fibrous interior.
An important characteristic that sets false morels apart from true, early, and bell morels is that false morels are hollow but chambered. True, early, and bell morels are hollow all throughout. False morels, meanwhile, have several hollow pockets inside of them.
Perhaps the most important thing to remember about false morels is that they’re known to be toxic, especially when they’re raw. They contain a compound called gyromitrin, which breaks down into monomethylhydrazine (MMH) when consumed. MMH can affect major organs in the body and cause severe poisoning.
There are those who still consume false morels after extensive cooking and preparation, but it’s important to keep in mind that these mushrooms can still be highly toxic even when cooked. Thus, it’s best to stay away from false morels and to leave them be when you encounter them.
Stinkhorn
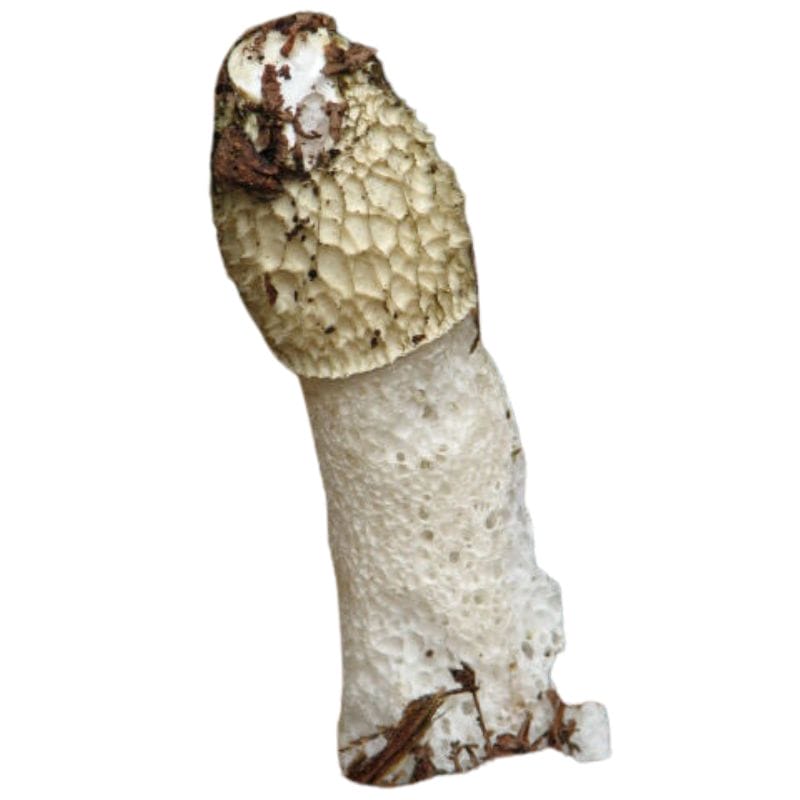

Stinkhorns are a group of mushrooms that certainly live up to their name. Aside from their distinctive appearance, they also have a distinctive smell. They have a strong, foul odor that’s often compared to the smell of rotting meat or even sewage. In fact, the smell alone can help you distinguish them from true morels.
Several stinkhorn species have a slimy mass on their caps. This mass is the gleba, or the spore mass. Because stinkhorns emit a foul, rotting smell, the often attract flies that then carry off the spores and spread them.
The caps of stinkhorns themselves are often slimy to the touch as well, as opposed to the dry caps of true morels. Depending on the species, stinkhorn caps can be pointed, rounded, or latticed. Stinkhorn are also soft and spongy, while true morel caps are firmer.
You can also differentiate between stinkhorns and true morels based on their habitats. While true morels generally thrive in hardwood forests and post-burn areas, stinkhorns grow in things like mulch, compost, and areas with decaying wood. They also prefer warm and humid environments.
How To Find Morels
Let’s get more specific and break down the different conditions in which morels can typically be found:
Know your trees if you want to find morels
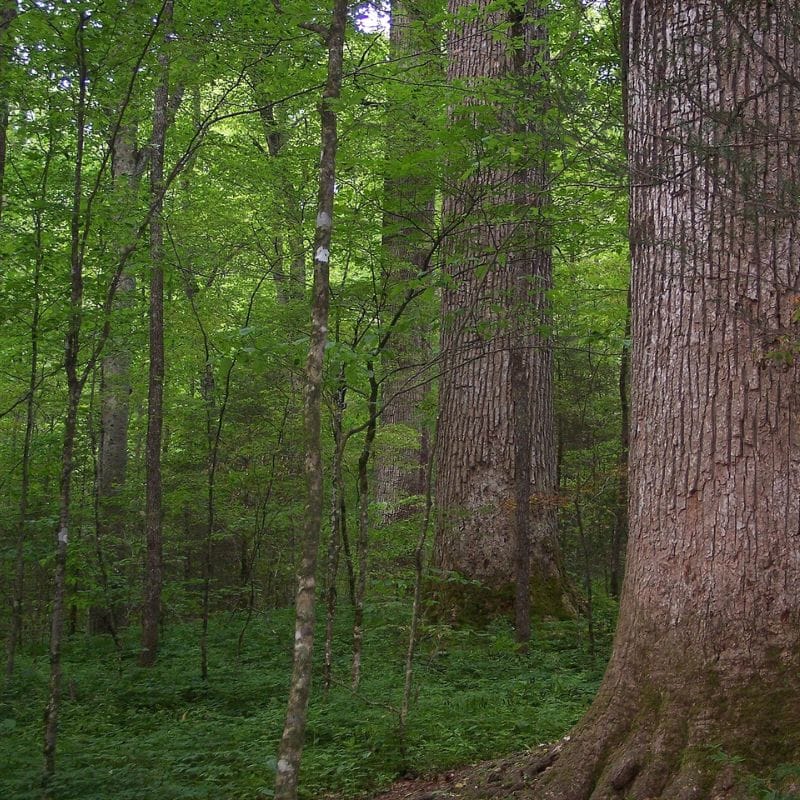

The most common type of trees associated with true morels are hardwood trees. You’ll often find morels at the base of these trees, around fallen leaves, or near decaying roots.
Keep an eye out for the following tree types:
- Apple
- Ash
- Aspen
- Douglas Fir
- Elm
- Oak
- Peart
- Ponderosa Pine
- Sycamore
- Tulip Poplar
- White Pine
If you need a refresher on how to identify these, you can check out this article on how to identify the trees morels love here.
Loamy or moist and well-drained soils around these trees are usually the best spots where morels can be found.
Coniferous trees are often associated with morels, though these are for fire-associated varieties. You can search for morels in conifer forests in the aftermath of a fire.
Moist soil near creeks and streams are ideal
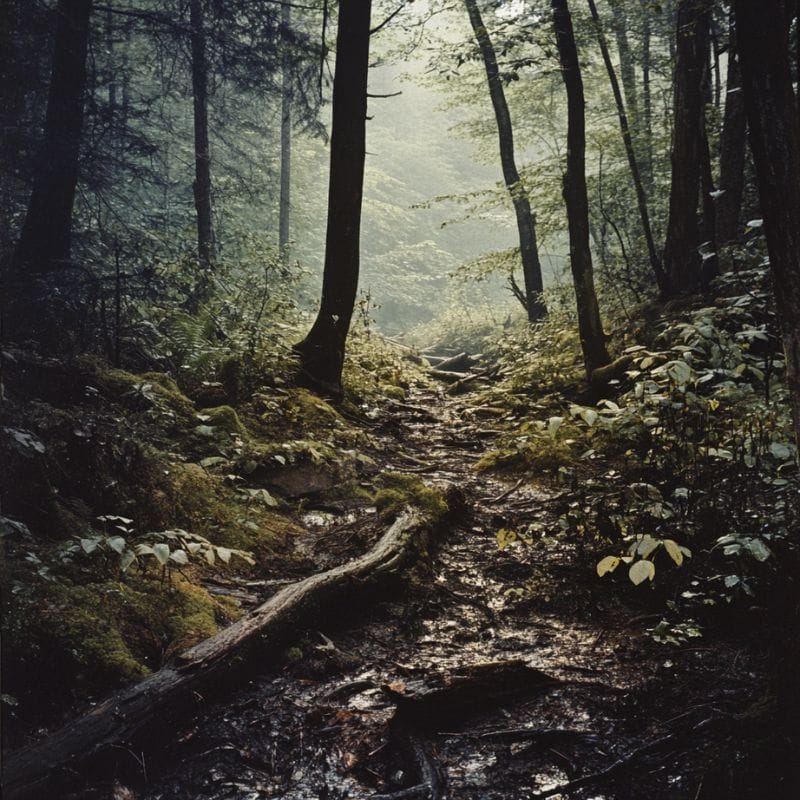

You’ll also be able to find morels in rich, moist soils near streams and creeks, especially those on hillsides.
However, it’s important to note that the area should have well-drained soil. That’s the type of soil that morels thrive in. You’re far less likely to find these mushrooms in wet, inundated soil.
Thus, when you’re near a stream or creek, try to go a bit farther away and look for spots where the soil drainage is much better.
Seek Out Old Apple Orchards
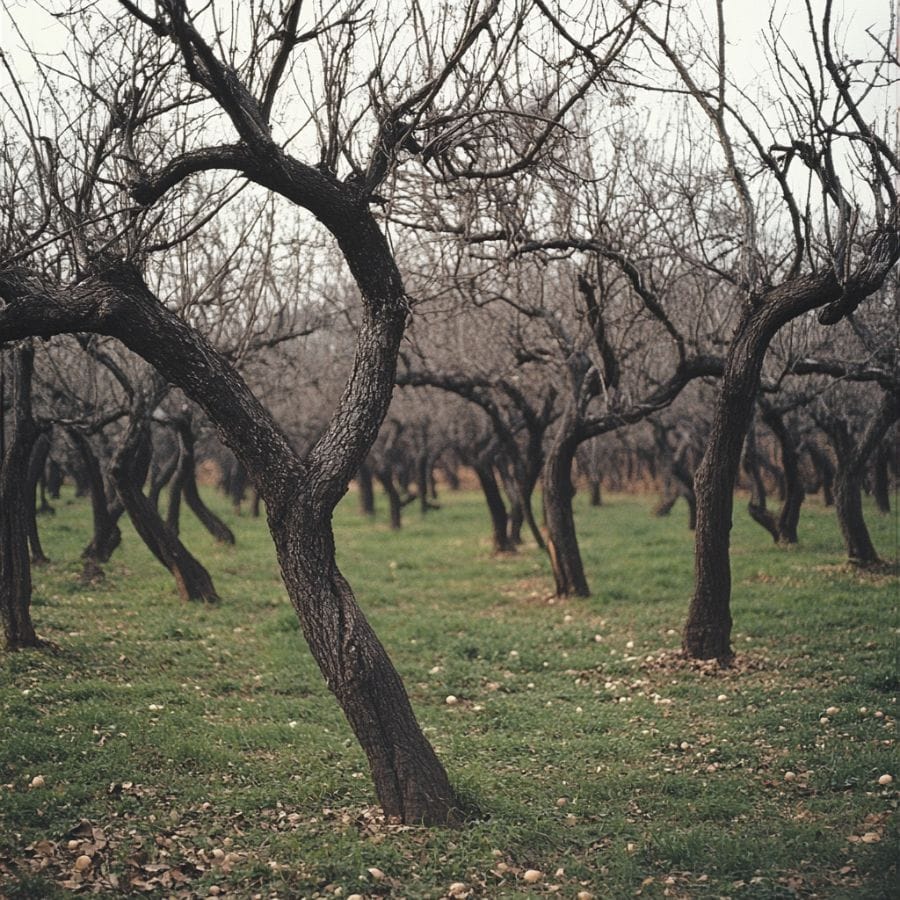

Morels notoriously thrive in old apple orchards, especially orchards in regions where apples have been historically cultivated. This is because morels are known to favor areas with decaying organic matter from dead or dying trees, and apple orchards are a prime candidate.
These old orchards often have decaying apple tree roots. The soil there is also often rich in nutrients and is well-drained, forming a great environment for morels to form.
Additionally, apple orchards have disturbed ground as a result of tilling and the removal of trees. This is yet another condition that morels prefer.
However, one caveat is that old apple orchards, especially those from the early to mid-20th century, were typically treated with pesticides like DDT and lead arsenates. These pesticides have been banned, but they’re still a concern. DDT takes a long time to break down, and lead isn’t biodegradable at all.
Thus, old apple orchards might be contaminated with these pesticides.
If you’re looking to broaden your spring foraging knowledge, these simple foods to forage in spring can be found in many of the same environments as morels.
Soil temperature is critical

Another environmental aspect that’s crucial for the growth of morels is soil temperature. Typically, the most ideal temperatures for morels to thrive are 50°F to around 55°F.
Morels might start appearing once temperatures reach around 48°F, continuing to thrive once temperatures are in the ideal range. They can still continue growing in the 55°F to 60°F range.
However, if temperatures rise too quickly, that might signal the end of morel season. Anything above 60°F will cause morels to begin to dry out and decay.
Focus on southward and westward slopes early in the season
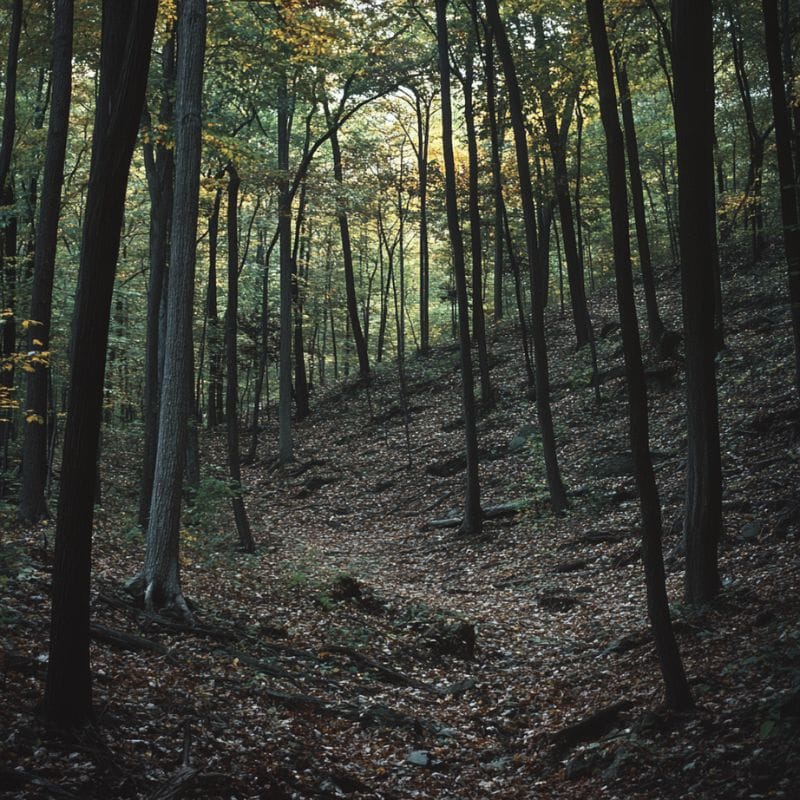

Morels tend to show up sooner on south- and west-facing slopes. This is because these slopes generally receive more direct sunlight, which makes them warm up faster in the spring. Thus, the soil here reaches the ideal 55°F to 60°F temperature range more quickly.
If you want to go morel hunting earlier in the season, you can check out south- and west-facing slopes. However, morels in these areas tend to be smaller and drier because of the higher temperatures.
Wait a little longer and you can hunt on north- and east-facing slopes. These areas won’t get as much direct sunlight and therefore warm up more slowly. Soils here also retain moisture much longer.
Thus, morels tend to be larger on north- and east-facing slopes, and they typically stick around for a longer period of time.
Burned areas are great for some morels
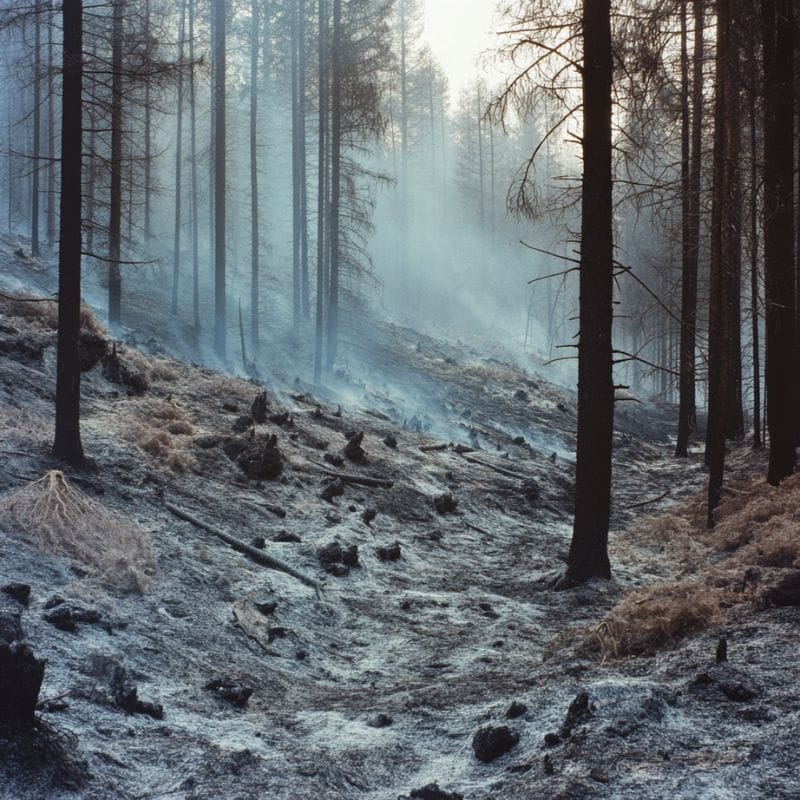

Burn areas are also a great place for morels to grow in, particularly those areas in the western US where wildfires occur frequently. You can expect morels to grow during the first spring following a wildfire.
Fire can give morels an advantage. For one thing, it can wipe out other fungi and plants that would compete with morels for nutrients. Morels also thrive in disturbed ground, of which there are plenty after a fire.
However, morels won’t thrive if the fire is too intense. The fire should just be intense enough that it can clear the forest floor without being so hot that it sterilizes the ground.
Tools from the ultimate forager’s toolkit can make searching in post-fire terrain much easier.
Rotting wood debris and leaves
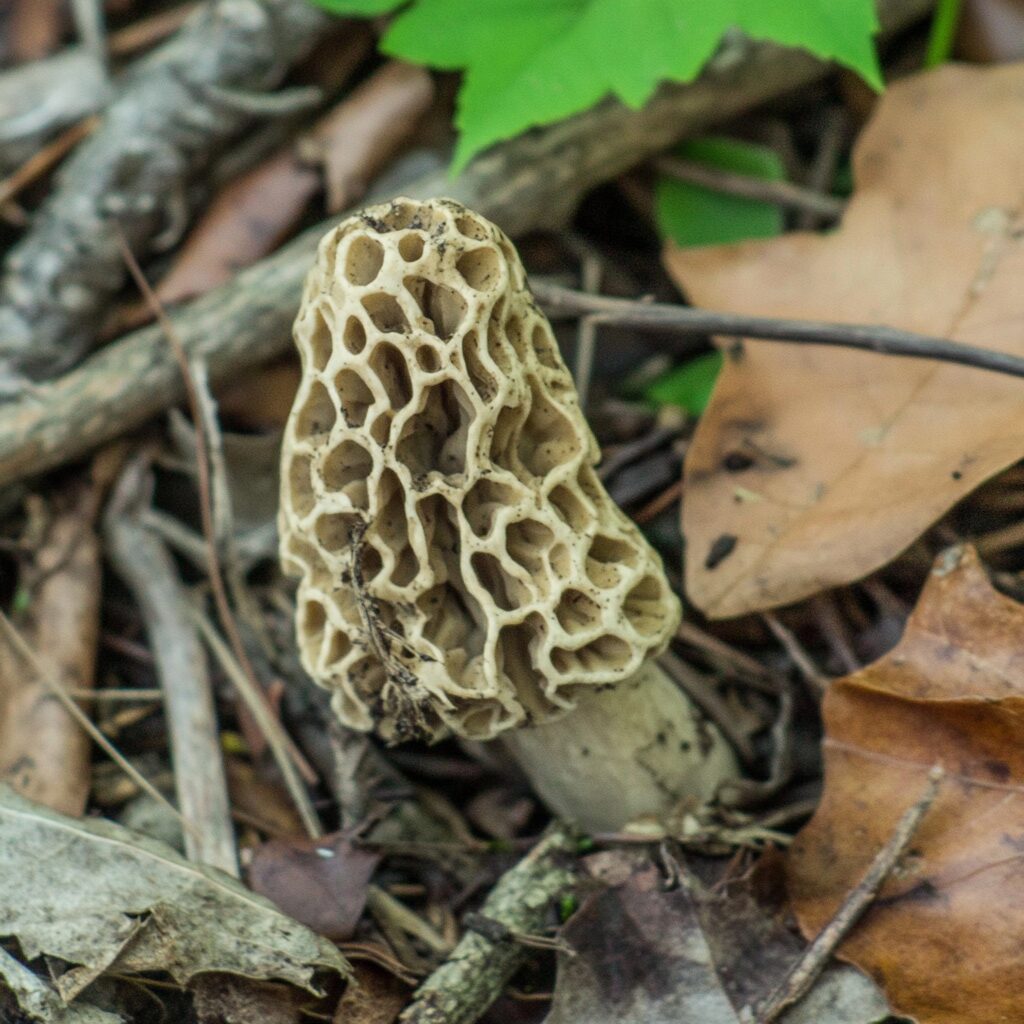

Look for spots where there are dead or dying trees, fallen branches, or fallen leaves. The roots and stumps of elm, poplar, ash, apple, and other types of hardwood trees in particular are also good places to look. These are prime spots for morels because decaying organic matter enables these mushrooms to thrive.
Decomposing leaves, wood, and roots release nutrients that fuel the growth of morels and other types of fungi. Decaying matter also holds the right amount of moisture that morels prefer.
When you see one there are often others nearby
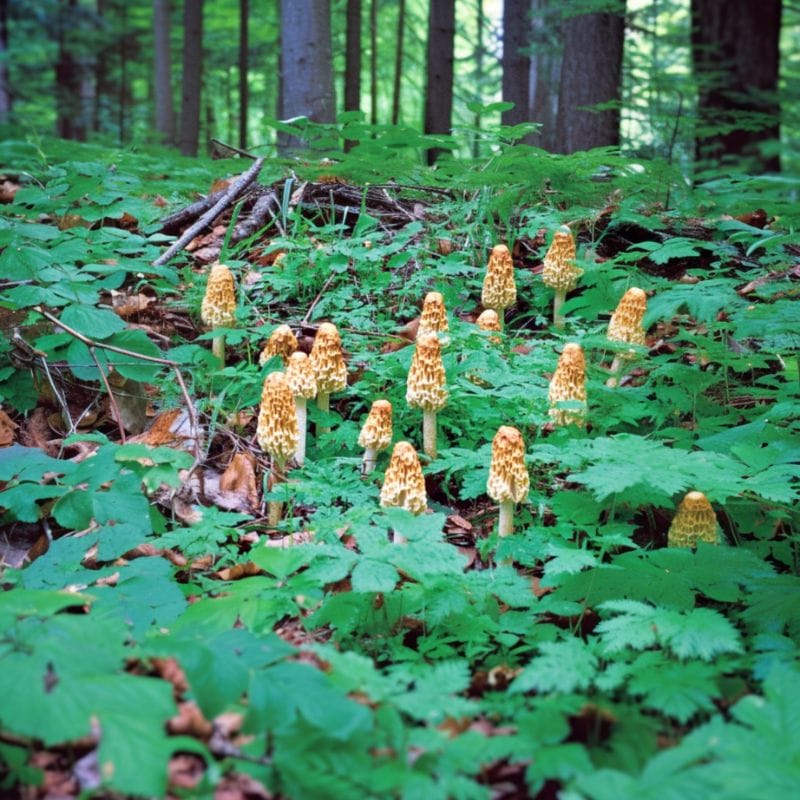

There’s rarely ever just one morel in a general area. Typically, they appear in small clusters. If you find one, it’s highly likely that there are more nearby, often within a distance of a few feet. You won’t find morels tightly packed together, but you won’t have to look far either for more specimens.
Morels can also return to the same spots year after year, though this is highly dependent on the conditions in the area. As long as all the right environmental conditions are there, you can come back to the same spots where you found morels every year. There will likely be more morels waiting.
It’s also possibly that these spots might shift slightly as time passes. Drastic changes, such as fires and floods, can also increase the chances of morels fruiting.
Old timers look to oak leaves and lilacs

Experienced foragers will likely tell you to keep an eye out for lilac blooms. This is because the conditions needed for morels to grow and lilacs to bloom are generally aligned. You’ll likely hear that morel season coincides with the blooming of lilacs, especially in temperate areas.
The emergence of oak leaves is also a traditional indicator for morel season, and with good reason. Oak leaves come out when temperatures reach the 50°F to 55°F range, so morels are not far behind. Once these leaves are roughly the size of a mouse’s ear, it’s time to start looking!
Before you head out
Before embarking on any foraging activities, it is essential to understand and follow local laws and guidelines. Always confirm that you have permission to access any land and obtain permission from landowners if you are foraging on private property. Trespassing or foraging without permission is illegal and disrespectful.
For public lands, familiarize yourself with the foraging regulations, as some areas may restrict or prohibit the collection of mushrooms or other wild foods. These regulations and laws are frequently changing so always verify them before heading out to hunt. What we have listed below may be out of date and inaccurate as a result.
Where You Can Find Morels
Armed with the knowledge of the typical places where morels can be found, we can now take a look at the places where you can go mushroom hunting successfully.
If you’re hoping to find other spring edibles along the way, these easy-to-identify wild roots and tubers are often found in the same environments.
These are some of the best spots for morels in the state:
Tombigbee National Forest

Tombigbee National Forest is a vast woodland area in the northeastern part of the state, covering more than 67,000 acres. The soil in Tombigbee is rich in nutrients and retains moisture well, creating ideal growing conditions. Many small streams crisscross the forest, contributing to the damp environment morels prefer.
Look for morels near dying elm trees or in areas where forest fires happened in previous years. Creek beds offer another promising hunting ground because morels enjoy the damp soil conditions.
Experienced mushroom hunters often suggest checking south-facing slopes early in the season as these areas warm up faster. The forest has many accessible trails that make it easier to explore different parts without getting lost.
Remember to bring a mesh bag for collecting so spores can fall as you walk, helping to spread more mushrooms for future seasons.
Delta National Forest

Delta National Forest, located between the Yazoo and Mississippi Rivers, holds the distinction of being America’s only bottomland hardwood national forest. This unique ecosystem spans about 60,000 acres of wetland in the Mississippi Alluvial Valley.
For successful morel hunting in Delta National Forest, concentrate on slightly elevated areas that don’t remain submerged during wet periods. The forest’s extensive network of old logging roads provides excellent access points for foraging adventures.
Look around mature ash trees and dying elms, which typically have symbiotic relationships with morel fungi. Transition zones between regularly flooded areas and higher ground can be especially productive hunting grounds.
The forest’s unique ecology creates diverse microclimates where temperature and moisture levels vary, potentially extending the morel season longer than in other Mississippi forests.
Holly Springs National Forest

Holly Springs National Forest encompasses about 156,000 acres in the north-central region of Mississippi near the Tennessee border. The terrain features beautiful rolling hills with numerous small streams creating a varied landscape.
The forest’s understory is rich with plant life and natural mulch that provides the organic material morels need to grow. This diverse environment includes both pine plantations and old-growth hardwood sections, offering different foraging opportunities.
The abundant creek bottoms provide excellent morel hunting grounds since they offer the right balance of moisture without being too wet. When searching, concentrate on the hardwood sections with ash, elm, and oak trees where morels typically form their mycorrhizal relationships.
Check areas with old fruit trees, as morels sometimes fruit near these locations. Try exploring less-traveled paths away from main trails where competition from other foragers is minimal.
Homochitto National Forest

Homochitto National Forest stretches across approximately 191,000 acres in the southwestern part of the state. Named after the Homochitto River that runs through it, this forest is characterized by deep ravines, clear streams, and hilly terrain.
The diverse topography creates many microenvironments where fungi can flourish. Homochitto’s soil has a distinctive mix of sandy and loamy textures that provides proper drainage while retaining enough moisture for mushroom growth.
The forest’s ravines can be particularly productive as they create protected microclimates with ideal growing conditions for morels. Moist bottomlands near the numerous water sources often yield good results for mushroom hunters.
Check areas with a thin layer of leaf litter where mushrooms can easily push through the surface. The mixed hardwood sections offer better hunting grounds than the pine-dominated areas.
Bienville National Forest

Bienville National Forest is located in central Mississippi, spanning 178,000 acres across Scott, Smith, Jasper, and Newton counties. Named after Jean-Baptiste Le Moyne de Bienville, a French colonizer and early governor of Louisiana, this forest features diverse terrain including rolling hills, flatwoods, and stream bottoms.
The mixture of pine plantations and natural hardwood stands creates varied ecosystems throughout the forest. Bienville’s rich biodiversity makes it an excellent habitat for wildlife and fungi alike.
The boundaries between different forest types can be productive areas to search as morels often appear in these transition zones. For successful hunting, the hardwood sections near streams and creeks offer prime locations with ideal moisture and soil composition.
Pay special attention to slightly disturbed soil areas where logging has occurred in previous years, as morels sometimes fruit abundantly in these locations. Look for areas with old-growth trees, particularly dying elms or ash trees that are starting to lose their bark.
The forest has several low-lying areas that maintain good moisture levels without becoming waterlogged, creating perfect conditions for morel growth.
Additional locations to find Morels
| Northern Mississippi | Morel Collection Details |
|---|---|
| George P. Cossar State Park | Morel mushroom collection is permitted for personal use. |
| Hugh White State Park | Visitors are allowed to gather morel mushrooms for personal consumption. |
| J.P. Coleman State Park | Individuals may collect morel mushrooms for their own use. |
| John W. Kyle State Park | Personal collection of morel mushrooms is allowed. |
| Lake Lowndes State Park | Morel mushrooms can be gathered by visitors for personal consumption. |
| Tishomingo State Park | Morel mushroom collection is permitted for personal use. |
| Central Mississippi | Morel Collection Details |
|---|---|
| Golden Memorial State Park | Visitors may collect morel mushrooms for personal consumption. |
| Holmes County State Park | Personal collection of morel mushrooms is permitted. |
| LeFleur’s Bluff State Park | Morel mushroom collection is allowed for personal use. |
| Roosevelt State Park | Visitors may gather morel mushrooms for personal consumption. |
| Trace State Park | Personal collection of morel mushrooms is permitted. |
| Southern Mississippi | Morel Collection Details |
|---|---|
| Buccaneer State Park | Morel mushroom collection is allowed for personal use. |
| Clarkco State Park | Visitors may collect morel mushrooms for personal consumption. |
| Flint Creek Water Park | Personal collection of morel mushrooms is permitted. |
| Paul B. Johnson State Park | Morel mushroom collection is allowed for personal use. |
| Percy Quin State Park | Visitors may gather morel mushrooms for personal consumption. |
| Shepard State Park | Personal collection of morel mushrooms is permitted. |
| Eastern Mississippi | Morel Collection Details |
|---|---|
| Clarkco State Park | Morel mushroom collection is allowed for personal use. |
| Lake Lowndes State Park | Visitors may collect morel mushrooms for personal consumption. |
| Legion State Park | Personal collection of morel mushrooms is permitted. |
| Nanih Waiya State Park | Morel mushroom collection is allowed for personal use. |
| Okatibbee Water Park | Visitors may gather morel mushrooms for personal consumption. |
| Western Mississippi | Morel Collection Details |
|---|---|
| Great River Road State Park | Personal collection of morel mushrooms is permitted. |
| Leroy Percy State Park | Morel mushroom collection is allowed for personal use. |
| Natchez State Park | Visitors may collect morel mushrooms for personal consumption. |
| Lake Chicot State Park | Personal collection of morel mushrooms is permitted. |
| Lake Washington | Morel mushroom collection is allowed for personal use. |
| Delta Region | Morel Collection Details |
|---|---|
| Delta National Forest | Visitors may collect morel mushrooms for personal consumption. |
| Malmaison Wildlife Management Area | Personal collection of morel mushrooms is permitted. |
| Mathews Brake National Wildlife Refuge | Morel mushroom collection is allowed for personal use. |
| Panther Swamp National Wildlife Refuge | Visitors may gather morel mushrooms for personal consumption. |
| Sunflower Wildlife Management Area | Personal collection of morel mushrooms is permitted. |
| Piney Woods Region | Morel Collection Details |
|---|---|
| Bienville National Forest | Personal collection of morel mushrooms is permitted. |
| Caney Creek Wildlife Management Area | Visitors may gather morel mushrooms for personal consumption. |
| Homochitto National Forest | Morel mushroom collection is allowed for personal use. |
| Leaf River Wildlife Management Area | Individuals are permitted to collect morel mushrooms for personal use. |
| Tallahala Wildlife Management Area | Visitors may collect morel mushrooms for their own consumption. |
| Coastal Region | Morel Collection Details |
|---|---|
| De Soto National Forest | Personal collection of morel mushrooms is permitted. |
| Pascagoula River Wildlife Management Area | Visitors may gather morel mushrooms for personal consumption. |
| Red Creek Wildlife Management Area | Morel mushroom collection is allowed for personal use. |
| Ward Bayou Wildlife Management Area | Individuals are permitted to collect morel mushrooms for personal use. |
| Wolf River Wildlife Management Area | Visitors may collect morel mushrooms for their own consumption. |
When You Can Find Morels

Morel mushrooms are known to show up in the spring, but exactly when is the question. The timing of morel season can vary, depending on the location, weather conditions, temperature, and various other factors.
In some areas, morels start emerging as early as the first few warm days after winter. If you’re in the southern United States, you might want to start morel hunting as early as March. If you’re in the northern parts of the country, such as the Midwest or the Northeast, you might have to wait until April to May.
Morels emerge later in the spring in some mountain regions, where morels season might continue up to early June. Typically, you can also expect fire morels to appear in the latter parts of spring.
Generally, you’ll want to hunt for morels a few days after some light rainfall, when temperatures start to get warmer. You can keep an eye on local weather forecasts, and you can also start checking soil temperatures if you haven’t done so yet. This can give you a much better idea of whether or not it’s time to put on your boots and start searching.
If you live in an area where wildfires occur, you might be able to start successfully searching for morels a day or two after a fire. However, keep in mind that other environmental conditions also need to be just right for morels to start fruiting. You might have to wait until later in the season, particularly in higher elevations.
It’s important to get the timing right! Morel season doesn’t last long, typically 4 to up to 8 weeks. This can also depend on a lot of different factors, many of which you can track and predict.
Thus, you need to make sure that you’re familiar with the topography and landscape of the area where you want to search, the weather, the environmental conditions, and the specific things that are conducive for morel growth. Make sure to get in early before all the good spots get wiped out!
As you head into peak season, it’s also worth learning about easy-to-identify wild nuts, seeds, and berries to round out your foraging haul.
One Final Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is for general informational and educational purposes only. Foraging for wild plants and mushrooms involves inherent risks. Some wild plants and mushrooms are toxic and can be easily mistaken for edible varieties.
Before ingesting anything, it should be identified with 100% certainty as edible by someone qualified and experienced in mushroom and plant identification, such as a professional mycologist or an expert forager. Misidentification can lead to serious illness or death.
All mushrooms and plants have the potential to cause severe adverse reactions in certain individuals, even death. If you are consuming foraged items, it is crucial to cook them thoroughly and properly and only eat a small portion to test for personal tolerance. Some people may have allergies or sensitivities to specific mushrooms and plants, even if they are considered safe for others.
Foraged items should always be fully cooked with proper instructions to ensure they are safe to eat. Many wild mushrooms and plants contain toxins and compounds that can be harmful if ingested.


