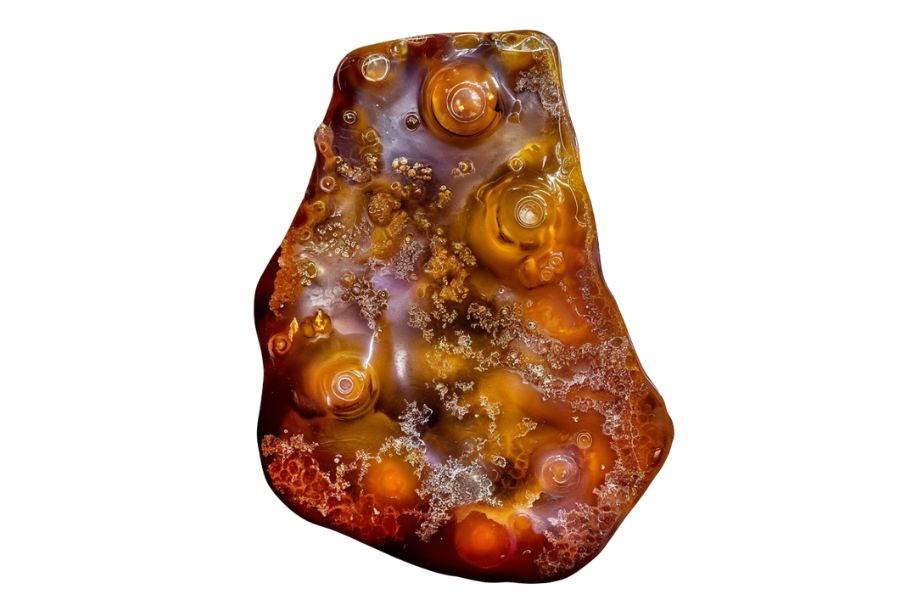
Fire agate hunting in Massachusetts is something I got into last summer. I never thought our state would have these gems until I found one right here in Massachusetts.
The rocks have this deep, warm glow when you hold them up to the light. They’re not super common, which makes finding one feel like winning a small lottery. I’ve spent many mornings walking creek beds and looking through old mining areas.
This state has some hidden spots where these stones form. Most tourists and even locals walk right past these areas without knowing what’s under their feet. The soil and rock conditions in certain parts of Massachusetts create the perfect environment for fire agates to develop over time.
While you hunt for fire agate, you will certainly find other interesting minerals. To ensure you can identify every potential treasure, Rock Chasing’s New England Rocks & Minerals Identification Field Guide is an indispensable resource.
It saves countless hours of research and prevents you from overlooking something valuable.
How Fire Agate Forms Here
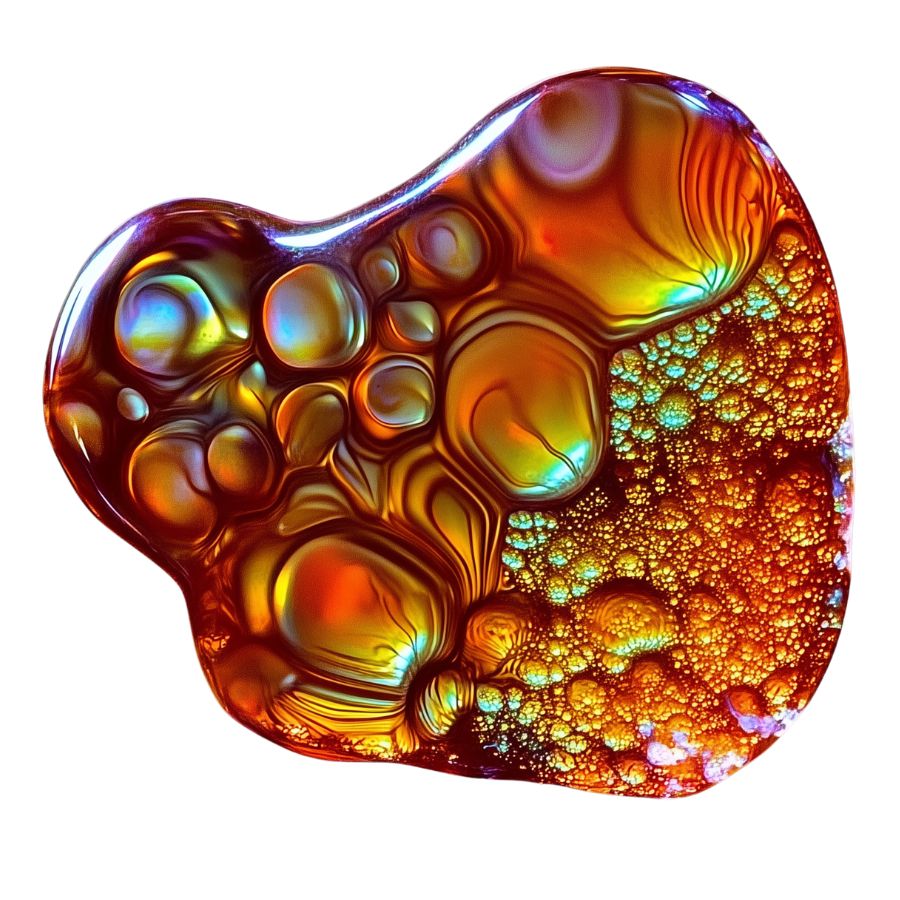
Fire Agate forms when silica-rich fluids seep into layers of chalcedony during volcanic activity. As these fluids cool down, they create super-thin layers of iron oxide and silica, kind of like stacking colorful sheets of plastic.
The iron oxide creates those beautiful iridescent colors you see – reds, oranges, and browns that seem to dance when you move the stone.
What’s really cool is that these layers are only about 0.5 microns thick (that’s thinner than a human hair!).
The more layers there are, the more intense the fire effect becomes. The whole process happens deep underground where hot water and minerals mix together over millions of years.
Types of Fire Agate
Fire agates represent nature’s artistry at its finest, showcasing spectacular plays of color that seem to dance within the stone. Each variety offers its own unique display of iridescent fire effects, created through millions of years of geological processes that layered minerals in distinctive patterns.
Brown Fire Agate
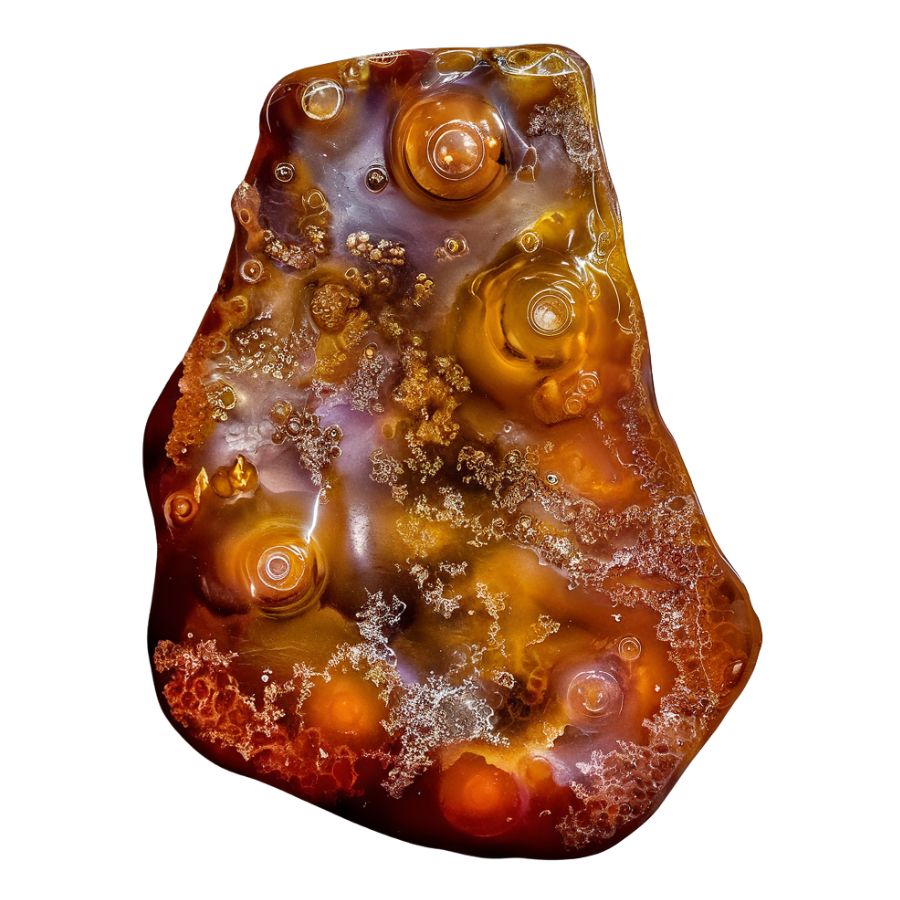
Brown Fire Agate displays a deep chocolate-brown base with brilliant flashes of color that dance across its surface. The most striking feature is how these colors appear to float at different depths within the stone, creating a three-dimensional effect.
The colors range from intense reds to bright oranges, often appearing in concentrated patches. The stone’s surface has a distinctive bubble-like texture that helps create its famous fire effect.
One special feature of Brown Fire Agate is its strong color concentration. The fire effect typically appears in bold, defined areas rather than being scattered throughout the stone.
Some exceptional pieces display color combinations that seem to shift and change as you move the stone, making each viewing angle unique.
You won’t believe how many incredible rocks and minerals you’ve walked past across New England without knowing their names.
This field guide makes it insanely easy to spot gems, minerals, and hidden treasures anywhere you explore.
📘 Check out the New England Field Guide Now →
What makes it different:
🚙 Field-tested across New England
📘 Heavy duty laminated pages resist dust, sweat, and water.
🧠 Zero fluff with clear visuals and straight-to-the-point info.
📍 Find hidden gems like Topaz, Amethyst, and beautiful crystals.
Orange Fire Agate
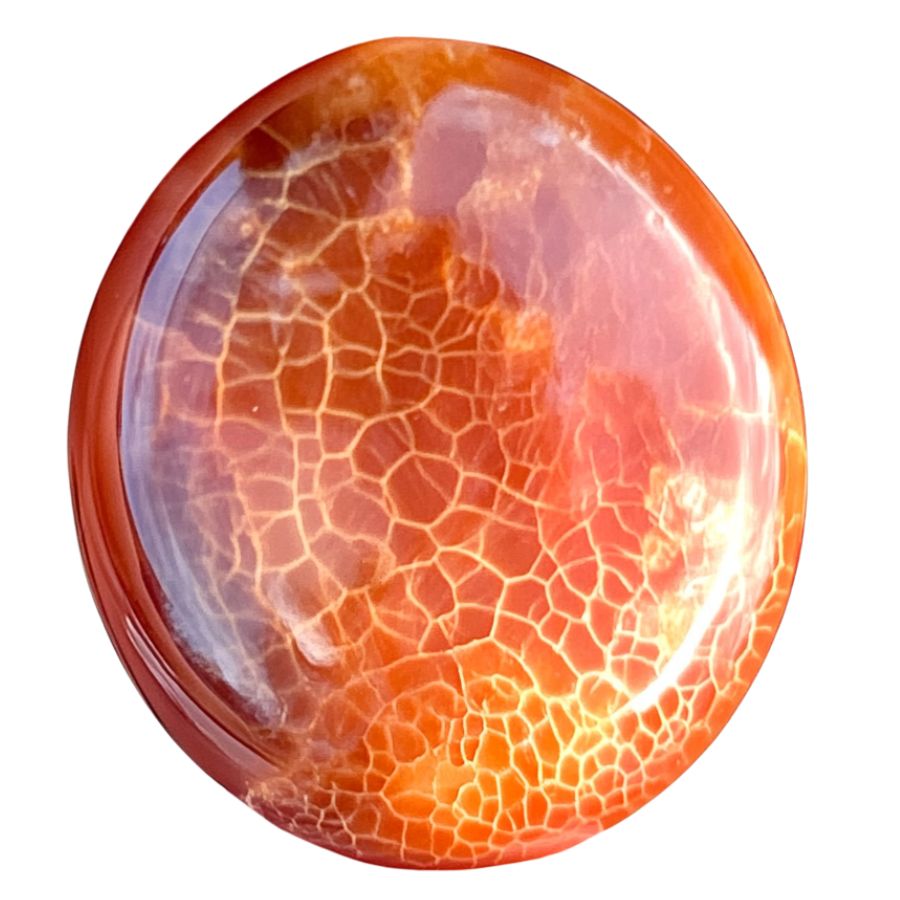

Orange Fire Agate shimmers with warm, sunset-like colors that seem to glow from within. The dominant orange tones mix with bright reds and yellows. These colors appear especially vibrant against the stone’s natural brown background.
The stone often shows interesting pattern formations that look like swirling flames or flowing liquid. These patterns form naturally during the stone’s creation and give each piece its own character.
A unique feature of Orange Fire Agate is its ability to show broad flashes of color. Instead of tiny specks, the color often appears in larger areas that create bold, dramatic effects.
The color layers in Orange Fire Agate often stack up in ways that create depth and dimension. When you look closely, you can see how these layers work together to produce the stone’s distinctive fire effect. The best pieces show clear, bright colors that remain visible from many different angles.
Yellow Fire Agate
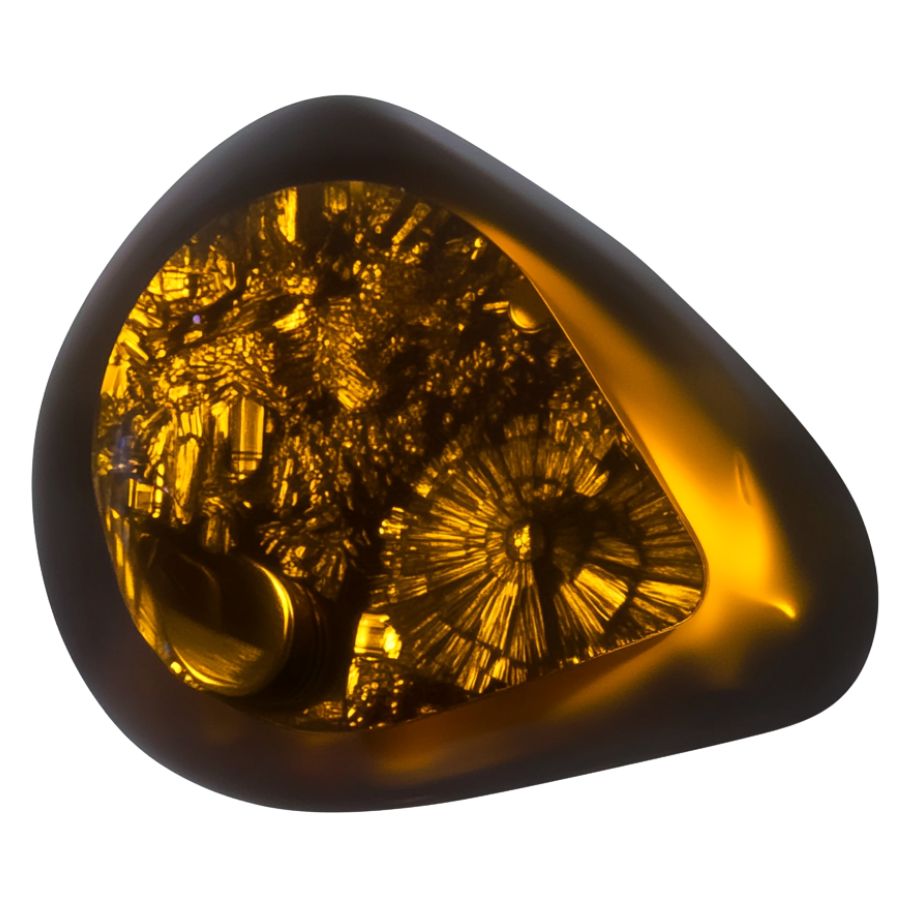

Yellow Fire Agate features bright, sunny yellow tones mixed with golden flashes that light up the stone. The yellow colors often appear alongside warm oranges and subtle greens, creating a bright, cheerful appearance.
Unlike other fire agates, the yellow variety often displays broader, more open patterns. This allows the yellow colors to spread out and create larger areas of bright color.
A special characteristic of Yellow Fire Agate is how its colors can shift between yellow and gold depending on the lighting. Sometimes, the stone shows unexpected flashes of green or blue, making it particularly interesting to observe.
The structure of Yellow Fire Agate often creates interesting patterns that look like sunbursts or radiating lines. These natural formations enhance the stone’s yellow tones and create fascinating visual effects.
Green Fire Agate
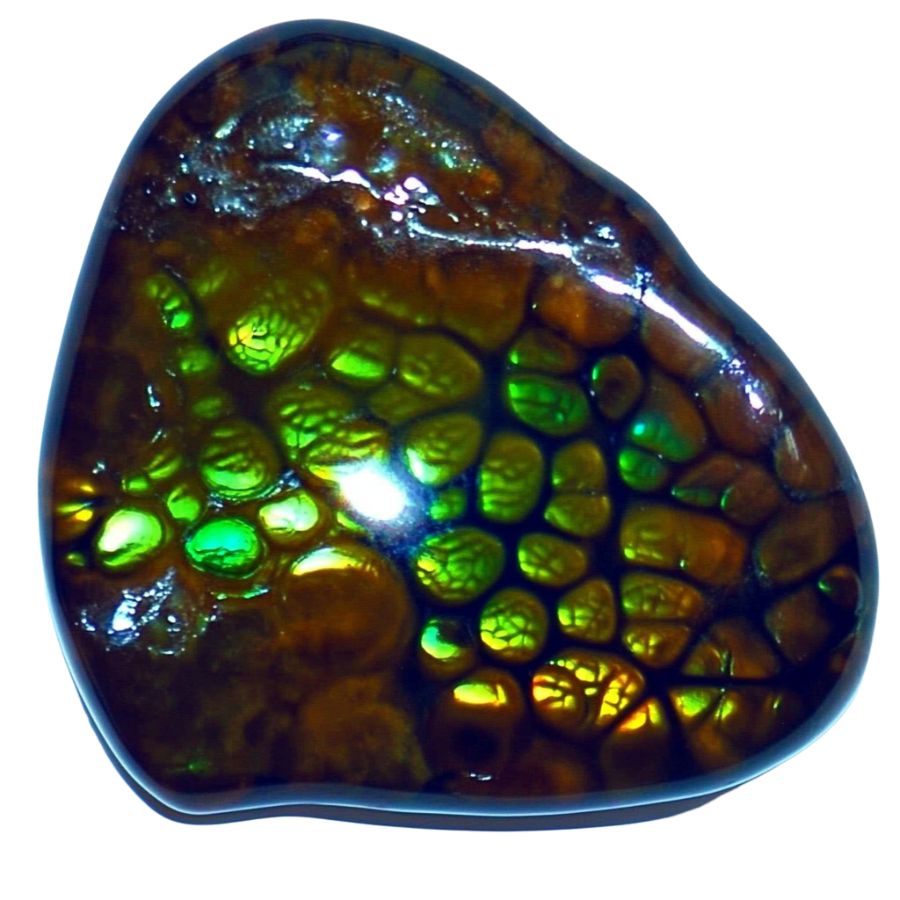

Green Fire Agate stands out with its unusual green flashes that sparkle against a dark background. This rare color combination creates an effect similar to the Northern Lights in miniature.
The green tones range from bright emerald to deep forest green, sometimes mixing with blue and turquoise highlights.
In natural sunlight, the greens become more vibrant and intense. Under artificial light, the stone might reveal subtle gold or blue undertones that weren’t visible before.
This stone sometimes shows an interesting phenomenon where the green fire appears to pulse or throb when the stone is moved. The combination of deep greens and shifting patterns creates a mesmerizing display that captivates viewers.
Peacock Fire Agate
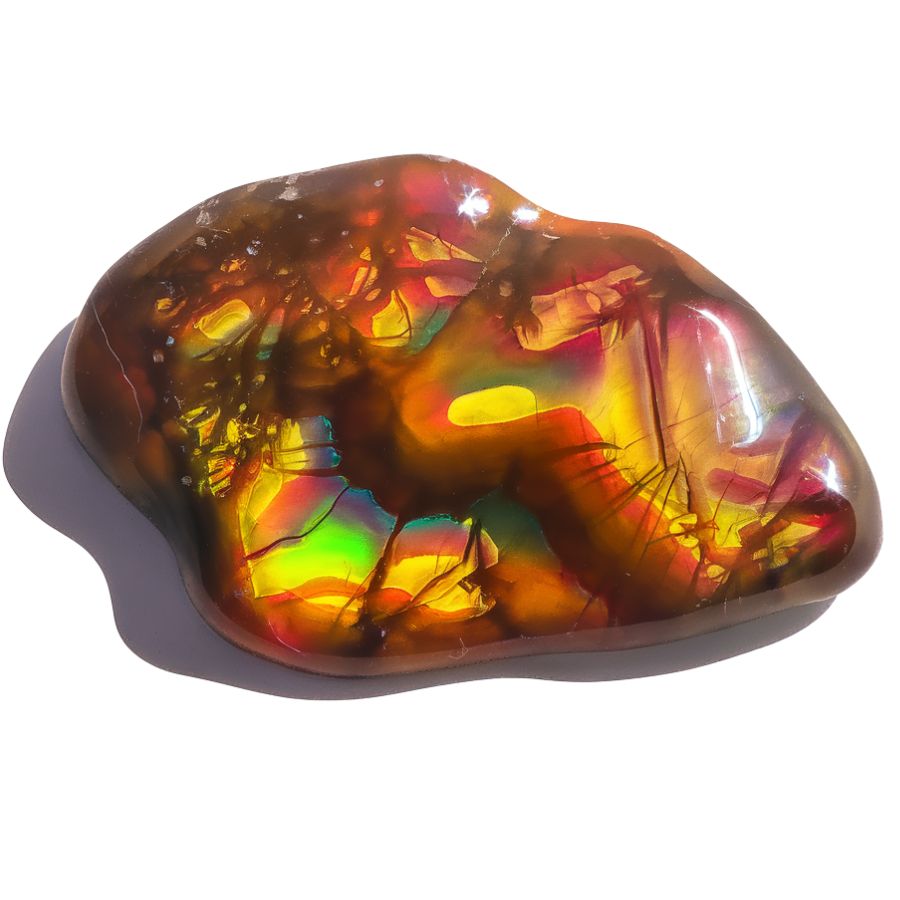

Peacock Fire Agate stands out for its remarkable display of iridescent colors that mirror a peacock’s feathers. The stone features bright greens, blues, and yellows that shimmer and change when viewed from different angles.
The stone’s surface has a unique grape-like structure called botryoidal formation. This creates small, rounded bumps across the surface that catch and reflect light in fascinating ways.
What makes this stone special is its ability to show three or more colors at once. While most fire agates display warm colors like orange and red, Peacock Fire Agate breaks this pattern with its cool, vibrant tones.
This variety requires skilled cutting to preserve its natural beauty. The cutting process must carefully consider the stone’s layers to maximize its color display and protect its delicate iridescent qualities. The end result is a stone that captures attention with its brilliant play of colors.
Crackled Fire Agate
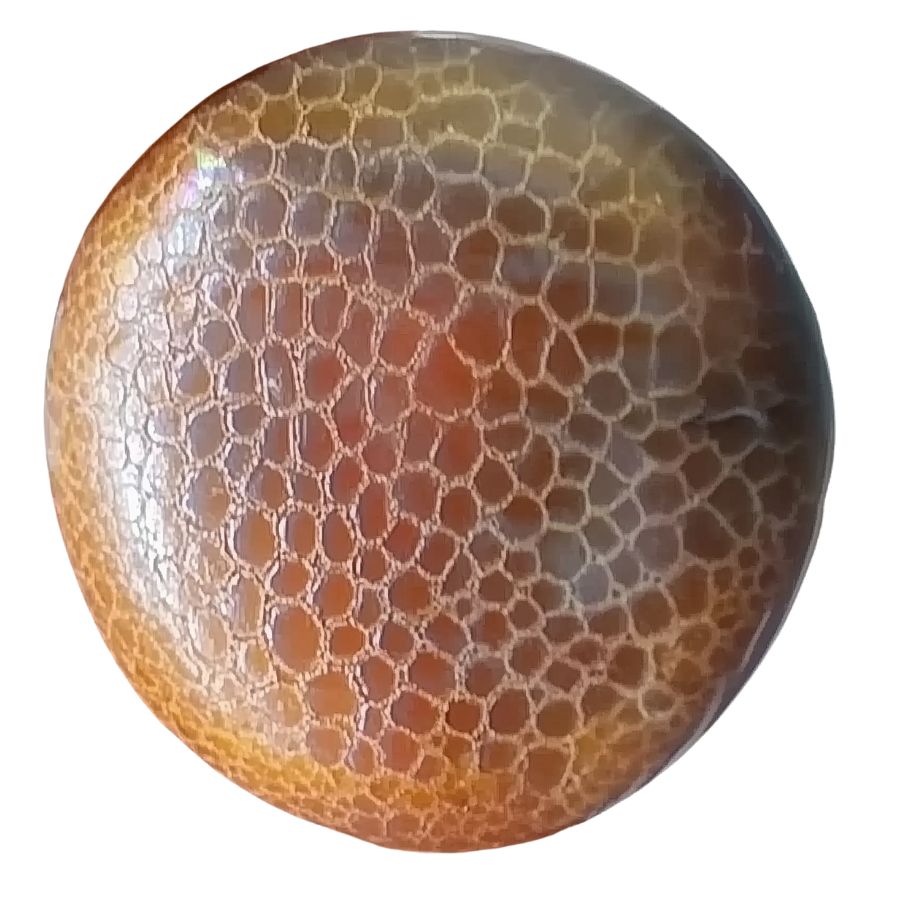

Crackled Fire Agate displays a deep reddish-brown base with bright flashes of orange, red, green, and gold. These colors create an effect that looks like flames trapped within the stone. The stone’s surface features a unique crackled pattern that resembles a spider’s web.
The stone gets its distinctive appearance through a special heat treatment process. The crackle effect adds depth and character to the stone’s natural fire-like appearance.
Unlike the uniform patterns seen in many stones, Crackled Fire Agate shows random, organic-looking designs. The combination of the crackled texture and the fire-like colors creates an impressive visual effect.
The complex internal structure of this stone makes it fascinating to observe. Light plays through the cracks and layers, creating an ever-changing display of colors. This interplay of light and pattern gives each stone its own personality and charm.
Mexican Fire Agate
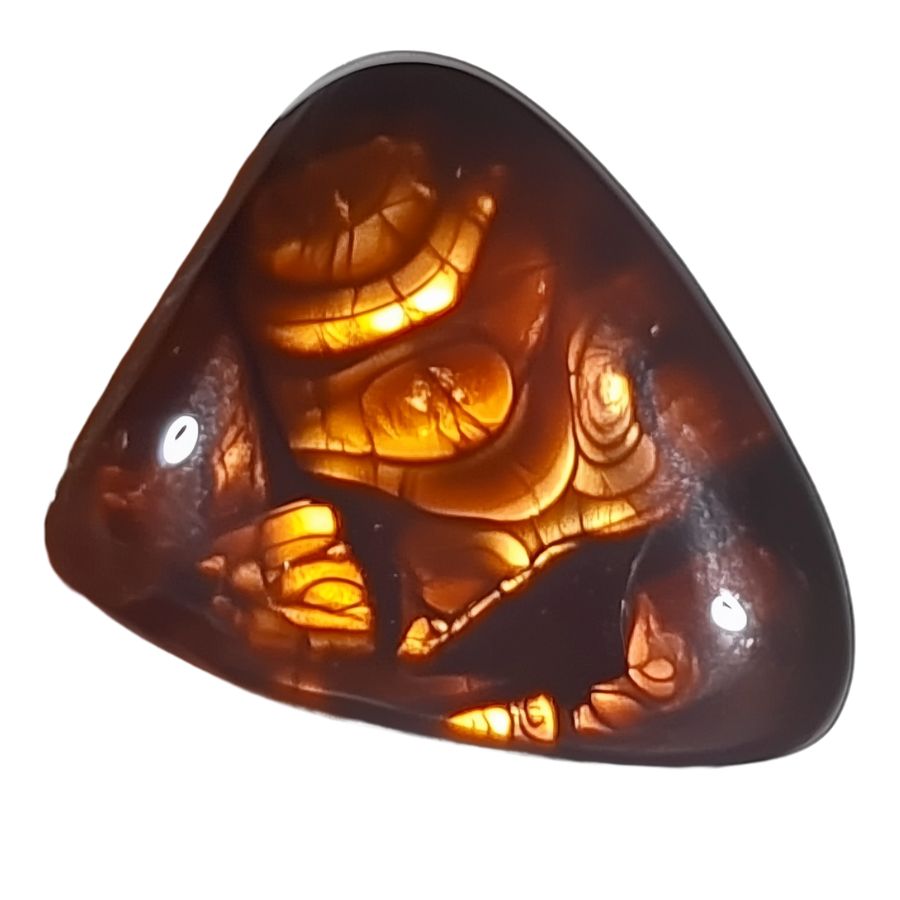

Mexican Fire Agate showcases brilliant flashes of color. The stone displays vivid reds, oranges, and yellows, with occasional hints of green and blue. These colors appear to move and shift within the stone, creating a dynamic visual effect.
The stone’s internal structure contains multiple thin layers that create its distinctive fire effect. These layers, built up over millions of years, catch and reflect light in unique ways.
Each piece of Mexican Fire Agate tells its own story through its pattern of colors. The stone’s surface often shows interesting textures and patterns that enhance its natural beauty. Some pieces display broad flashes of color, while others show intricate, detailed patterns.
The stone’s formation process gives it exceptional clarity and brightness. Unlike artificially enhanced stones, its beauty comes entirely from nature. .
Arizona Fire Agate
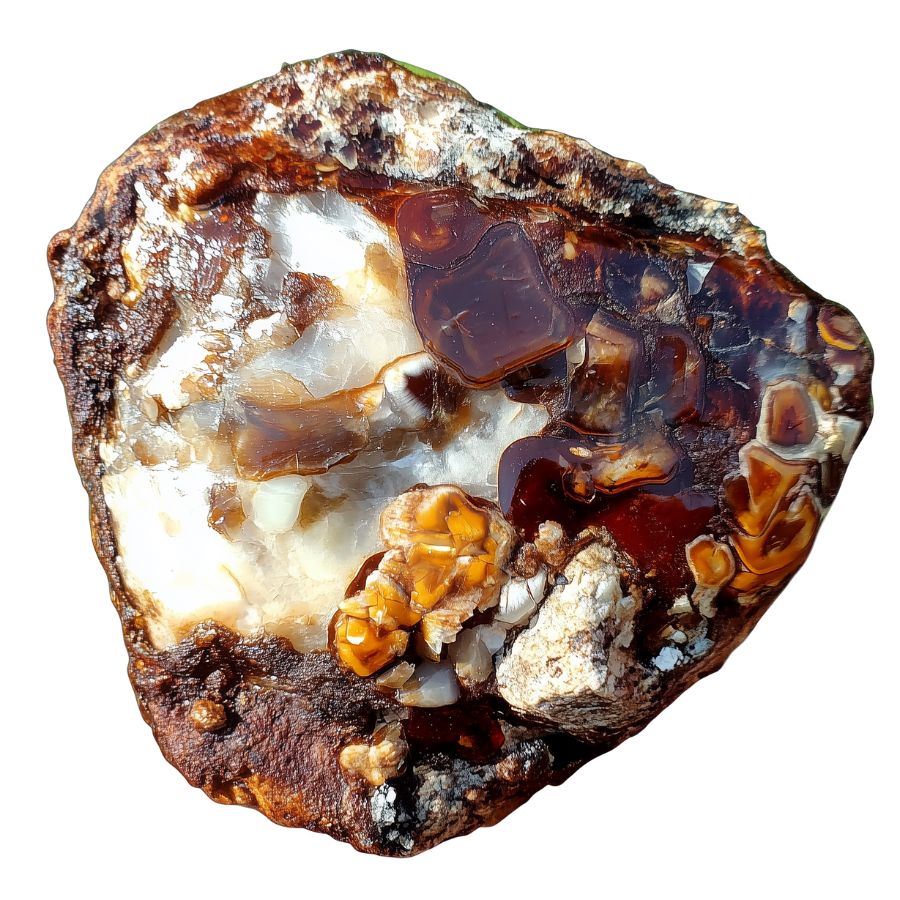

Arizona Fire Agate showcases a unique combination of a rich brown base with vibrant flashes of color. The stone’s distinguishing feature is its exceptional three-dimensional play of color, which appears to float within different layers.
It often shows stronger and more concentrated color patterns compared to other varieties. The fire effect typically appears in concentrated areas rather than spread throughout the stone.
This concentration creates dramatic focal points that catch the eye immediately. Many pieces display a distinct bull’s eye pattern where the colors radiate from a central point.
This stone is known for its durability and lasting color display. Unlike many other iridescent stones, its color effect doesn’t fade or diminish over time. The colors remain vivid even after years of exposure to light.
What Does Rough Fire Agate Look Like?
Here’s how you can identify a Fire Agate in its natural state.
Look for the Characteristic Brown Base Color
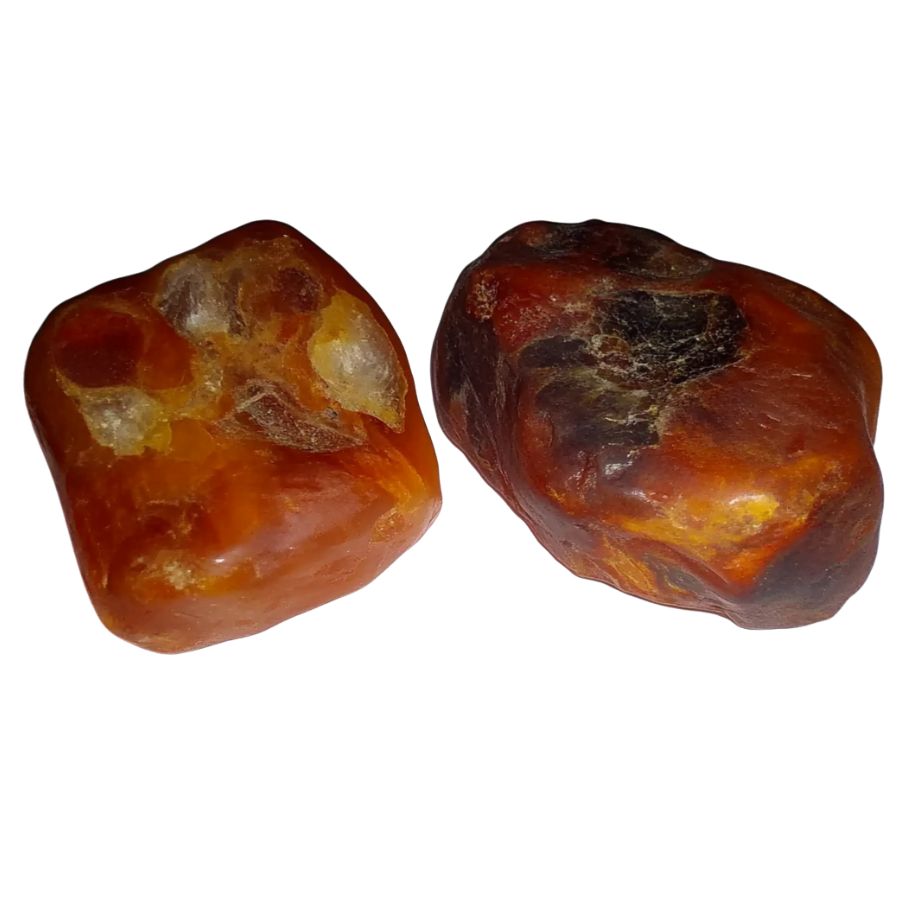

Raw fire agate typically shows up as a brownish-gray or reddish-brown nodule. Don’t expect the flashy colors right away! The base material looks pretty ordinary – like a dull, chocolate-colored rock.
Sometimes you’ll catch hints of that signature iridescence peeking through, especially in small cracks or worn areas.
Check for Botryoidal Surface Texture
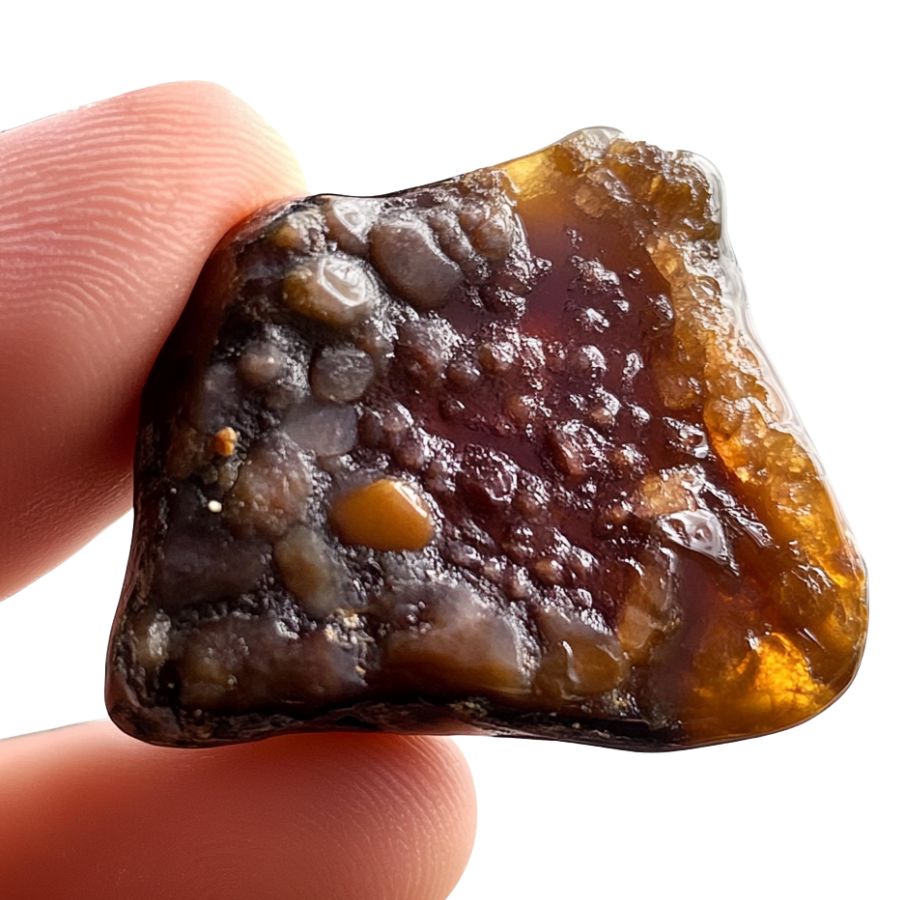

Run your fingers over the surface. Feel those grape-like bumps? That’s the botryoidal texture – a dead giveaway for fire agate.
These rounded bumps often cluster together, creating a bubbly surface that looks like frozen soap bubbles. Fresh pieces might have a crusty, rough coating hiding this texture.
Inspect for Color Play in Natural Light
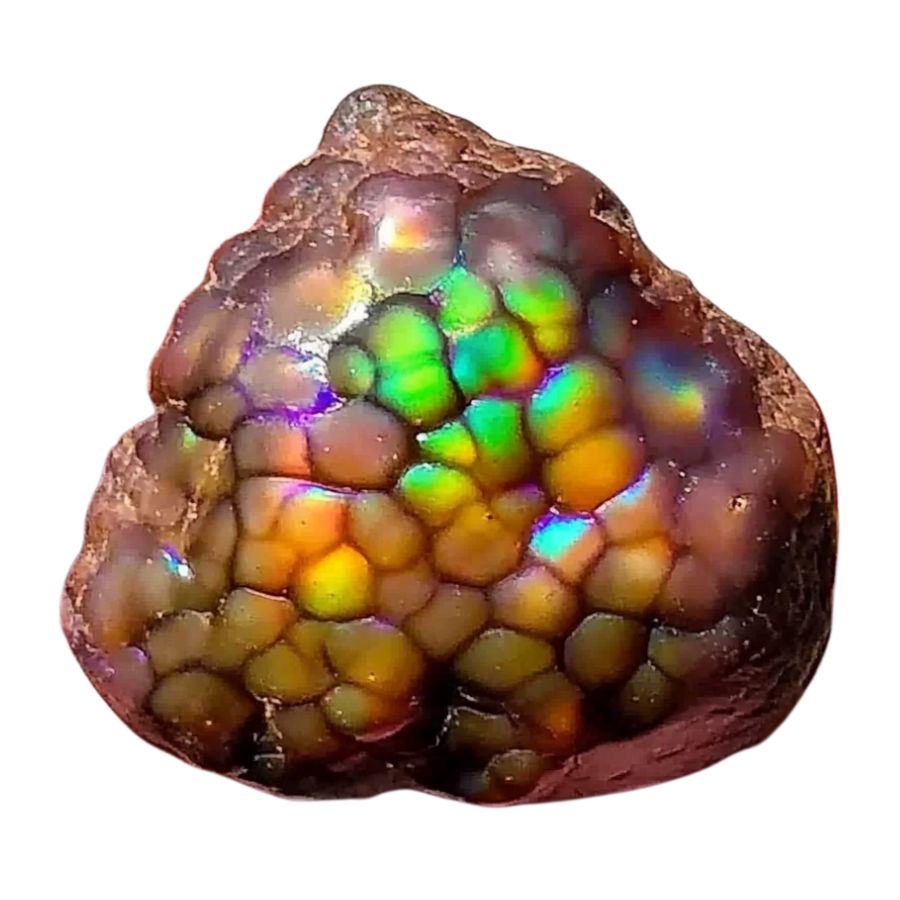
Hold the specimen under direct sunlight or bright light. Rotate it slowly. Look for flashes of green, gold, or red in small areas – especially where the surface is naturally worn.
These color flashes might be subtle in rough pieces, appearing like tiny windows of color.
Test the Chalcedony Properties
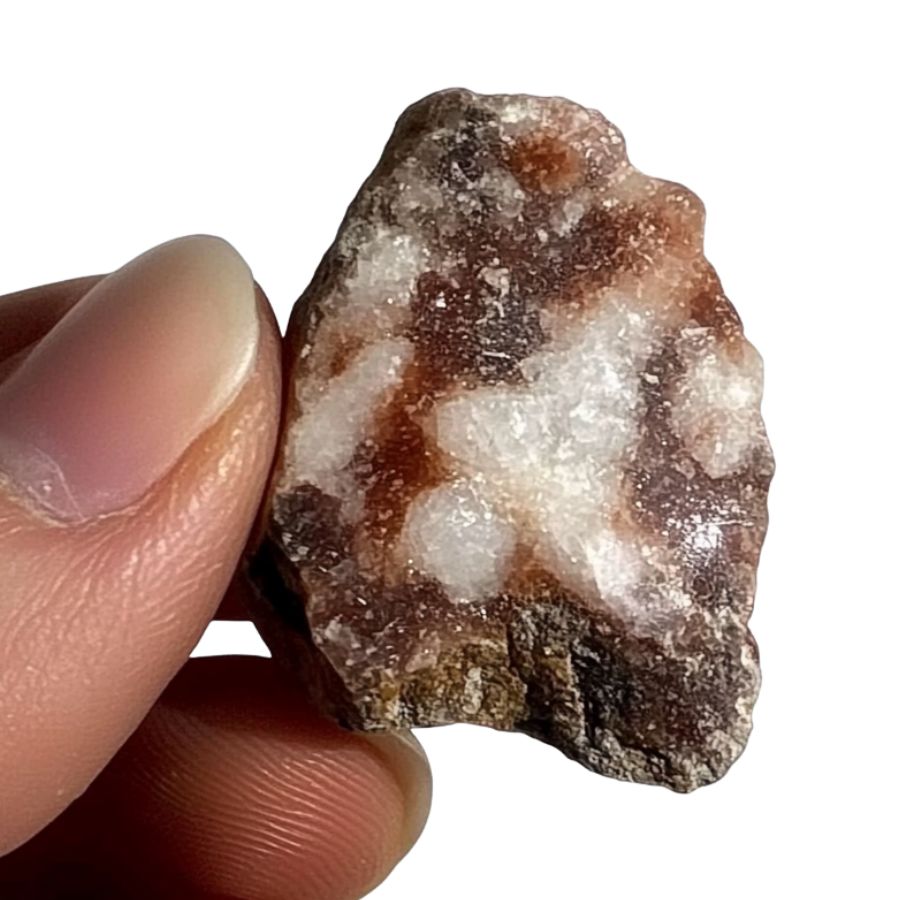

Fire agate is a variety of chalcedony, so it should feel quite solid and slightly warm to the touch. Try scratching it with a steel knife – it shouldn’t scratch easily.
The surface might show some waxy or glassy areas where the outer layer has worn away, revealing the chalcedony underneath.
Tips on Where to Look
Fire agate is found in areas with past volcanic activity. These beautiful stones typically form in volcanic regions where silica-rich solutions filled cavities in rocks. Here’s where you should start looking:
Volcanic Rock Formations
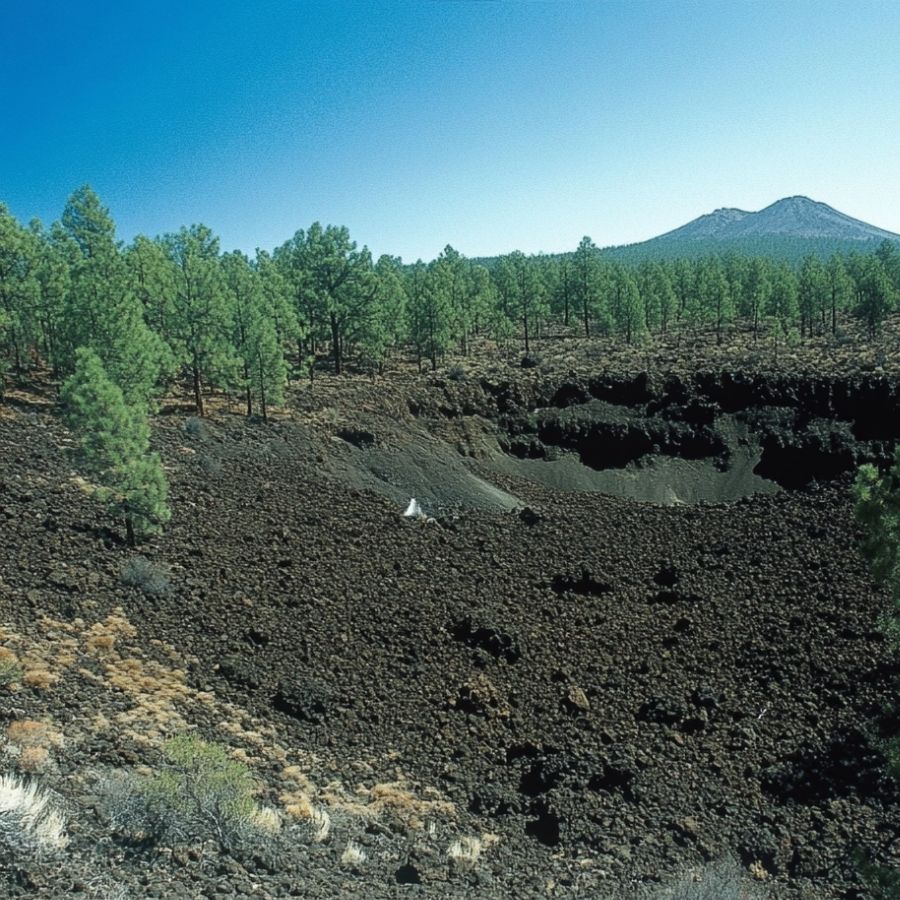

Look for areas with basalt or other volcanic rocks. The stone usually forms in gas pockets within these rocks. Check dark-colored, rough-textured rocks that seem bubbly or have lots of holes.
Areas where you spot chunks of obsidian are also promising, since both stones form in similar conditions.
Desert Washes and Dry Creek Beds
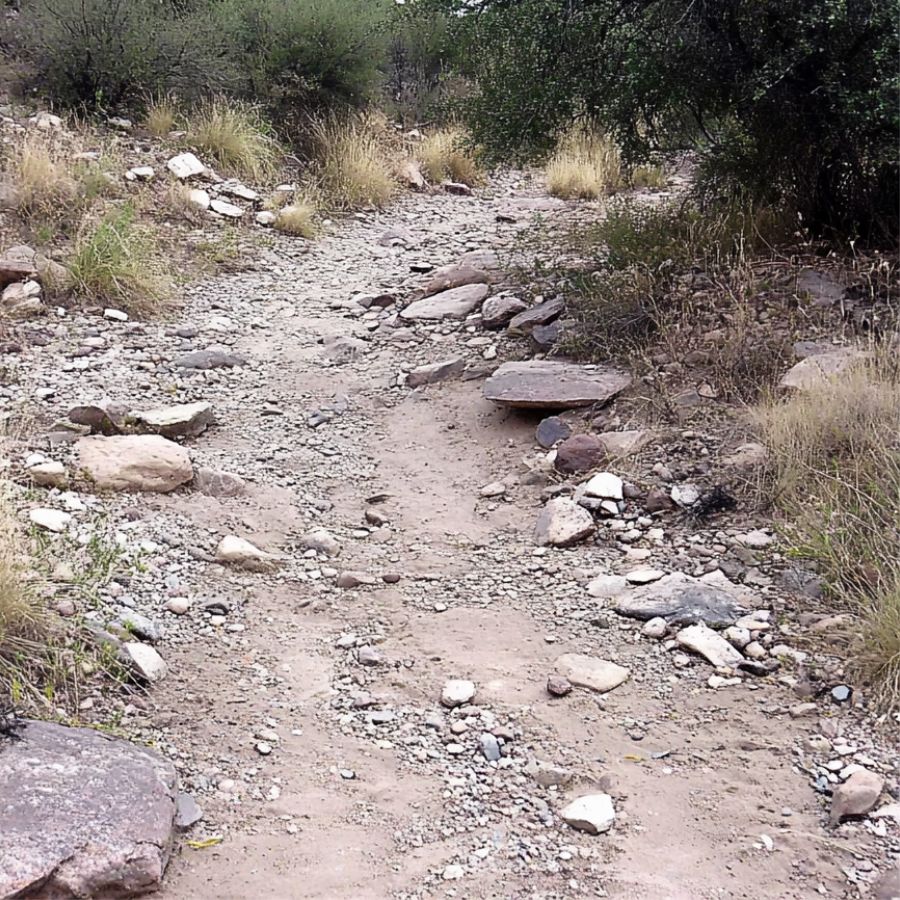

Search in dry creek beds that cut through volcanic areas. After rainstorms, these washes often expose new material and can reveal fire agate specimens that have weathered out of their host rock.
Keep an eye out for reddish-brown chunks with a waxy luster, which could be your target stone hiding under a chalcedony crust.
Old Mining Areas

Check around abandoned mining districts, especially those known for copper minerals. Fire agate often occurs near copper deposits, so tailings piles and dumps from old mines can be great spots to search.
When you’re exploring these areas, look for rocks with a botryoidal (grape-like) surface texture and reddish-brown coloring, which are typical characteristics of fire agate’s outer appearance.
Hillside Slopes

Explore gentle slopes below volcanic outcrops. As the host rock weathers, pieces of fire agate often roll downhill and collect along these slopes.
The best time to search these areas is after heavy rains have washed away loose soil and exposed new material, giving you a better chance of spotting the distinctive brown nodules that might contain fire agate.
Tools You Will Need
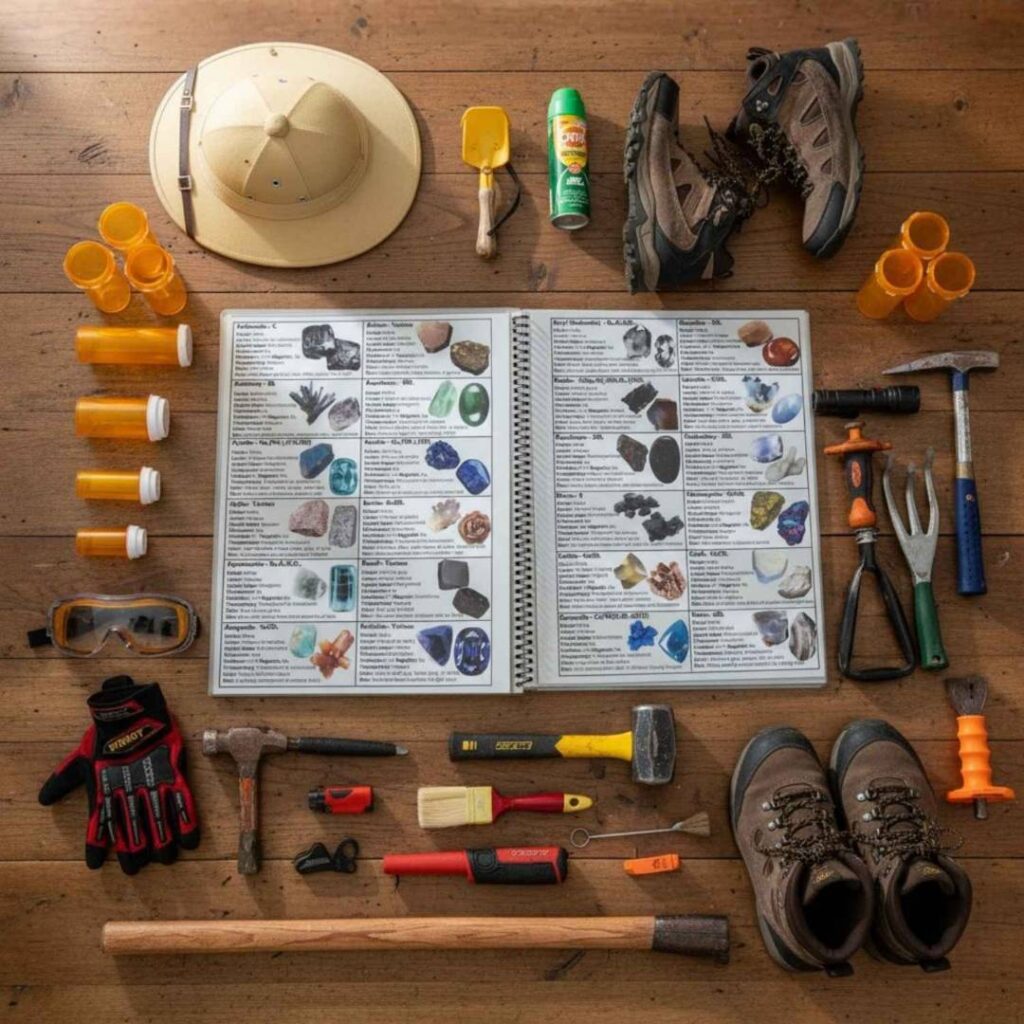

The hunt for fire agate is like looking for a hidden flame trapped inside a stone. This amazing gem has a secret rainbow of color, and you do not need much to begin the search. A few basic tools are all it takes to have a fun, safe, and maybe even successful adventure!
A Trustworthy Field Guide – Essential
The best part of rockhounding is often sharing the thrill of discovery with friends and family. A field guide becomes essential when it makes the hobby accessible and fun for everyone, turning a simple outdoor trip into a genuine treasure hunt.
This is exactly what Rock Chasing’s New England Rocks & Minerals Identification Field Guide is designed to accomplish. It makes identifying over 120 different minerals a fast and exciting experience for all ages by using over 300 vivid color photos rather than dense, complicated text.
Even kids and beginners can recognize real gems in the wild, making it a perfect tool for creating shared memories.
Because it’s built to be truly hands-on, with fully laminated, waterproof pages and a tough iron spiral binding, it’s a worry-free companion for years of family adventures, no matter the weather.
Safety Glasses – Essential
This is the most important tool you will carry, and it is not negotiable. Fire agate is found in hard host rock, and breaking it can create very sharp, fast-moving chips. A simple pair of safety glasses is essential for protecting your eyes from any debris.
Masonry Hammer – Essential
A masonry hammer is an excellent all-in-one tool for this type of hunting. It has a heavy, flat head for breaking larger rocks and a sharp, chisel-like tail on the other side. That chisel end is perfect for splitting rock layers apart to reveal the bubbly agate formations hidden inside.
Wearable Knee Pads – Recommended
Searching for fire agate often means spending a lot of time on your knees, closely examining the ground and sorting through rocks. A simple pair of wearable knee pads, like the kind used for gardening, makes this much more comfortable.
Water Spray Bottle – Optional
Dry fire agate can look dull and ordinary, hiding its internal fire. This is where a simple spray bottle filled with water becomes your secret weapon. A quick spritz on a promising stone will instantly reveal the gem’s colorful flash, helping you spot the real keepers.
Some Great Places To Start
Here are some of the better places in the state to start looking for fire agates:
Always Confirm Access and Collection Rules!
Before heading out to any of the locations on our list you need to confirm access requirements and collection rules for both public and private locations directly with the location. We haven’t personally verified every location and the access requirements and collection rules often change without notice.
Many of the locations we mention will not allow collecting but are still great places for those who love to find beautiful rocks and minerals in the wild without keeping them. We also can’t guarantee you will find anything in these locations since they are constantly changing.
Always get updated information directly from the source ahead of time to ensure responsible rockhounding. If you want even more current options it’s always a good idea to contact local rock and mineral clubs and groups
Ashmere Lake

Ashmere Lake is found in Hinsdale, Berkshire County. The lake has two parts: a shallow north side with lots of plants, and a deeper south side. The south basin has a bottom made of mud with large areas of rock and rubble, especially in the west and south parts.
Glaciers shaped the land around Ashmere Lake long ago. They left behind deposits containing lace agate pebbles and cobbles. Most agates here are white chalcedony with fine, delicate bands in grey colors.
However, Fire Agate can also be found here. You should check the western and southern shores of the southern basin for fire agates. The rocky areas along the shoreline are good spots to look, especially where waves have uncovered stones.
Also, look at the hillsides and slopes around the lake. These areas may have rock debris moved by gravity that could contain agates. The best time to search is after rain has washed away dirt, making the colorful stones easier to spot.
If your kids keep asking, “What rock is this?”, here’s your answer.
🪨 300+ bright, kid-friendly photos
💦 Waterproof and built for outdoor adventures
🔍 Simple explanations made for young explorers
🌲 Helps kids learn, play, and explore outdoors
This durable field guide shows them exactly what they found, fast, fun, and frustration-free.
Rochester
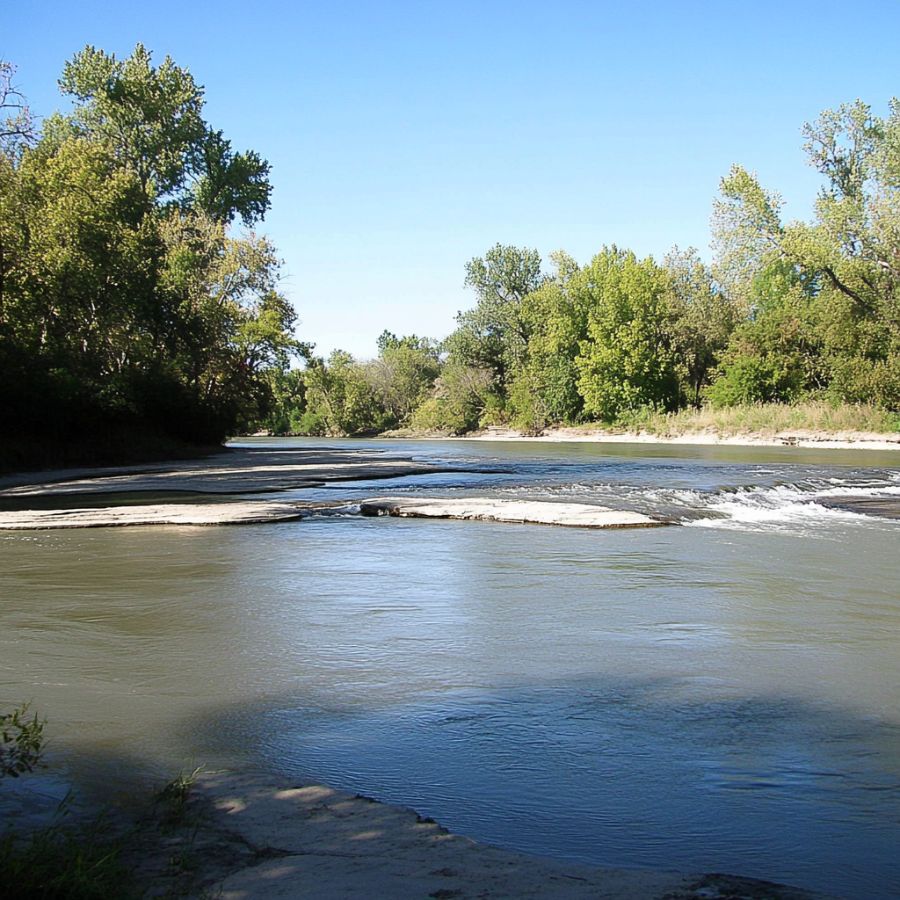

Rochester sits in Plymouth County. Founded in 1686, this town keeps its country feel with beautiful landscapes, farms, and natural areas. The town has many parks and trails for visitors to enjoy.
Ice Age glaciers shaped Rochester’s land. They left behind till, sand, and gravel deposits. The town’s bedrock includes granite and schist, which form the foundation of the area’s natural beauty.
You can search for Fire Agate in several places around Rochester. The northern parts toward Middleborough have been noted for agate findings. Southeastern areas extending to Fairhaven also show promise for collectors.
Local streams and riverbeds offer good hunting grounds too. Water naturally erodes and moves stones, often concentrating agate nodules in these areas. Bring rock hammers and sieves to help find and identify these beautiful stones with their unique play of colors.
Williamstown
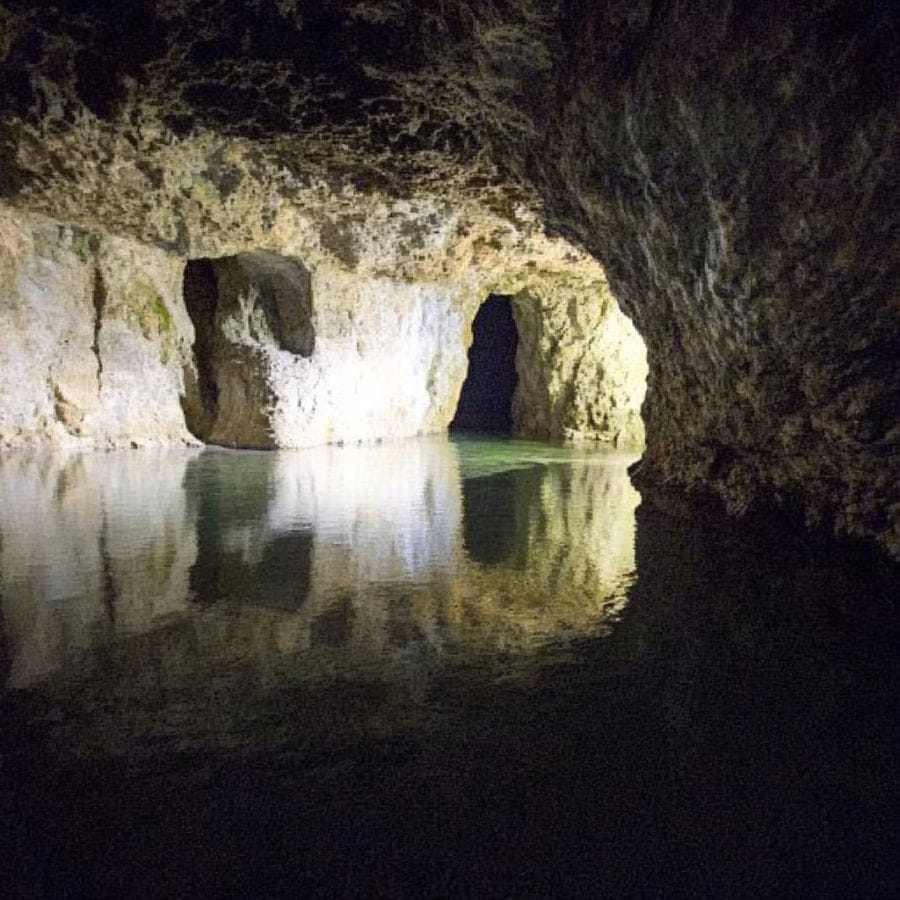

Williamstown is in the northwest corner of Berkshire County. Home to Williams College since 1793, the town mixes natural beauty with culture. The Clark Art Institute and Williamstown Theatre Festival add to its artistic scene. Mountains surround the town, creating stunning views.
The rocks in this area formed about 500 million years ago when tectonic plates crashed together. These collisions created huge mountains that have since worn down.
Rock collectors can visit several good spots. Pine Cobble, a 400-acre nature area, has interesting quartzite formations. Brodie Mountain shows off Ordovician phyllite and other metamorphic rocks.
For Fire Agate specifically, check the Hoosac River “Jasper” area, known for its chalcedony deposits. The old Mt. Prospect Lime-Marble Mines might also yield Fire Agate, especially where silica-rich fluids have moved through the marble.
Deerfield River
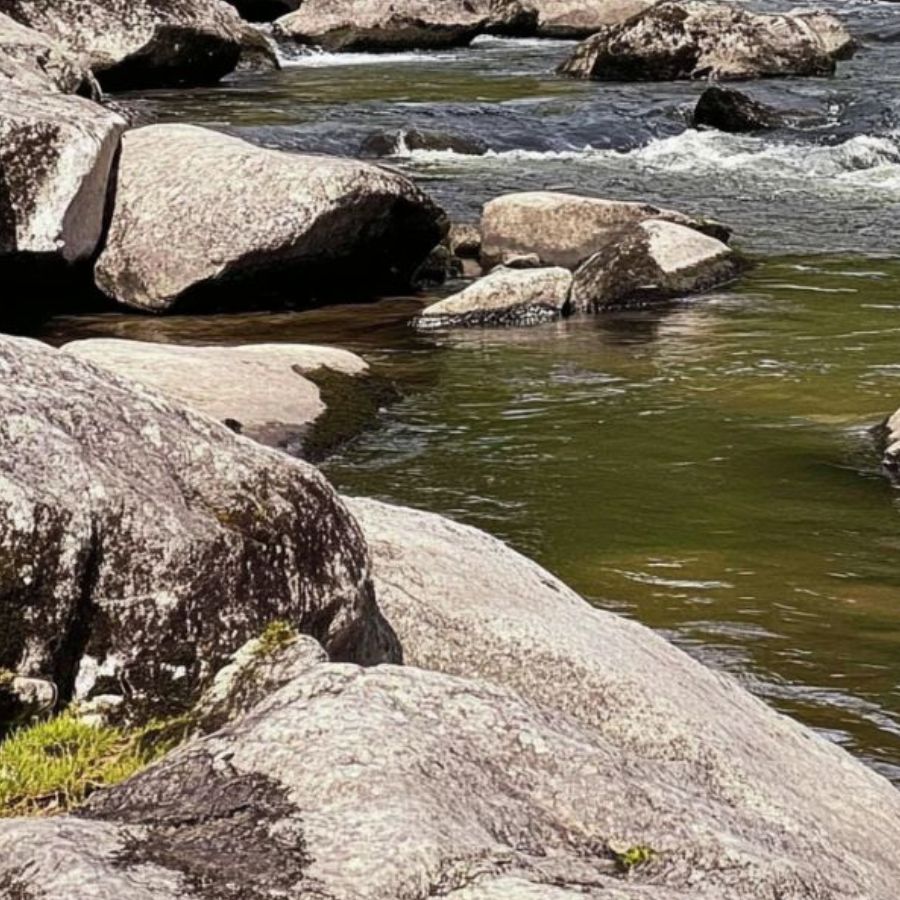

The Deerfield River flows for about 76 miles through northwestern Massachusetts. Starting in southern Vermont, it travels southeast through the Berkshire Mountains before joining the Connecticut River in Greenfield. The river features both calm sections and exciting rapids, making it popular for outdoor activities.
Glaciers carved the Deerfield River Valley during the last Ice Age. The area once lay under glacial Lake Hitchcock, which helped create special features like the “Glacial” Potholes at Shelburne Falls. These bowl-shaped holes were made by the river’s force and show off gneiss, a type of metamorphic rock.
Many rock collectors have found agate nodules, amethyst, and sometimes geodes along the river’s banks and gravel bars. The mix of sedimentary and metamorphic rocks in the area creates good conditions for these semi-precious stones.
To find Fire Agate, look along gravel bars and rocky outcrops by the riverbanks. Places where smaller streams join the main river often collect various mineral deposits.
Conway
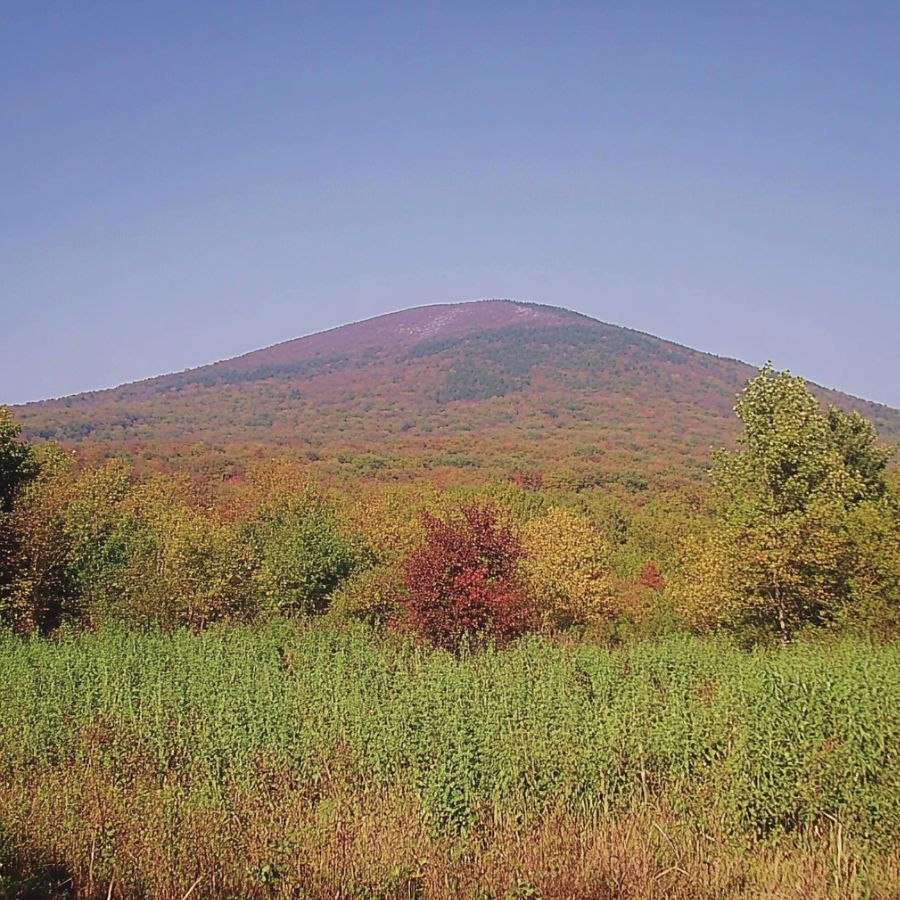

Conway is a small town in Franklin County. Created in 1767, it features rolling hills, thick forests, and beautiful farms. The peaceful setting shows off New England’s classic countryside charm.
Ancient forces and glaciers shaped Conway’s land over millions of years. The main rock type is Williamsburg Granodiorite, a coarse-grained igneous rock that pushed into surrounding rocks during the Devonian period. This rock makes up about 80% of the bedrock in the Avery Brook area of southwest Conway.
Throughout town, you’ll find outcroppings where bedrock breaks through the surface. These natural landmarks tell stories about the area’s geological past. Conway even has a silver mine, mentioned in old records. The Conway Silver Mine covers a large area and was once known for its silver ore.
Fire Agate searchers should visit the gravel pits in the Conway and Amherst area. These sites have produced various agate specimens. The area near Cold River has also been noted for agate finds.
Places Fire Agate has been found by County
After discussing our top picks, we wanted to discuss the other places on our list. Below is a list of the additional locations along with a breakdown of each place by county.
| County | Location |
| Hampshire | Betts Manganese Mine |
| Hampden | Hampden Quarry |
| Middlesex | PJ Keating Quarry |
| Worcester | Bolton Lime Quarry |
| Franklin | Route 2 Road Cuts |
| Franklin | Turners Falls |
| Bristol | Gooseberry Island |
| Barnstable | Sandwich Beaches |
| Worcester | Forty Caves |
| Hampshire | Plainfield Area |
| Hampshire | Goshen Stone Quarries |
| Hampden | Mount Tom |
| Bristol | Dighton Rock Area |
| Bristol | Horseneck Beach |
| Franklin | Shelburne Falls Area |




